Figure 1.
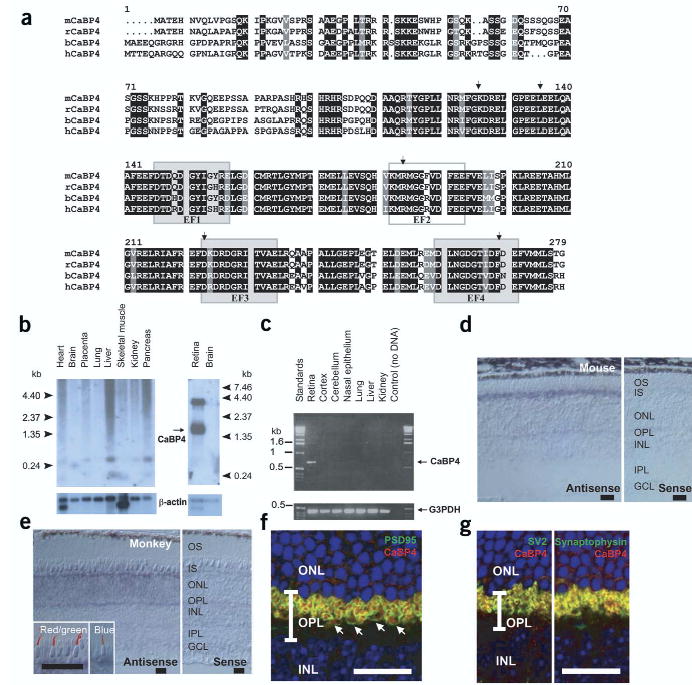
CaBP4 protein sequence, tissue distribution and immunolocalization. (a) Primary structure of mouse (m), rat (r), bovine (b) and human (h) CaBP4 (accession numbers AY039218, XM_344981, AY048883 and AY039271). The identical residues in all sequences are in white on a black background. Conservative substitutions are in white on a gray background. Functional EF-hand motifs are shown as shaded boxes and nonfunctional EF-hand motif as an open box. Arrows indicate the intronexon junction of the CABP4 gene. (b) Northern blot analysis of CaBP4 mRNA from various human (left) or rat (right) tissues. Control hybridization with a 32P-labeled β-actin mRNA is also shown. (c) PCR analysis of CaBP4 transcript in various mouse tissues. A positive control was carried out with primers specific for glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (G3PDH). (d) In situ hybridization of CaBP4 transcripts in mouse retina using antisense (left) and sense (right) RNA. (e) In situ hybridization of CaBP4 transcripts in monkey retina using antisense (left) and sense (right) RNA. Inset, immunoreactivity with antibodies to red and green opsin (left) and blue opsin (right) was covisualized with CaBP4 transcripts (blue signal). (f) Presynaptic localization of mouse CaBP4 (red) demonstrated by covisualization with a presynaptic protein (PSD95; green). Arrows indicate rod spherules and cone pedicles. (g) Colocalization of synaptic vesicle proteins SV2 and synaptophysin (green) with mouse CaBP4 (red). In f and g, yellow indicates overlap of two immunoreactivities and blue indicates cell nuclei (Hoechst 33342 staining). INL, inner nuclear layer; ONL, outer nuclear layer; OPL, outer plexiform layer. (d–f) Scale bars, 20 μm.
