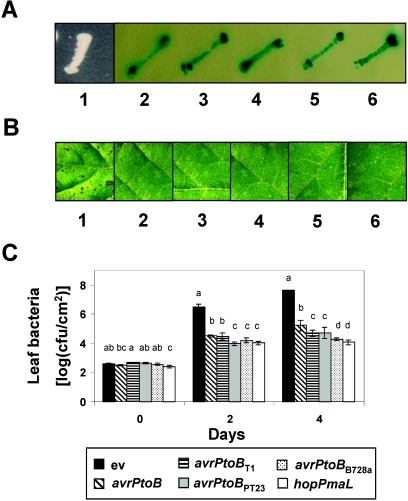
FIG. 4.
AvrPtoB homologs interact with Pto and elicit Pto-dependent resistance. (A) Yeast two-hybrid interactions of Pto with AvrPto or the AvrPtoB homologs. Image 1, empty vector; image 2, AvrPtoB; image 3, AvrPtoBT1; image 4, AvrPtoBPT23; image 5, AvrPtoBB728a; image 6, HopPmaL. (B) Elicitation of Pto-dependent resistance by infiltration of RG-PtoR leaves with 104 CFU ml−1 ΔavrPtoΔavrPtoB expressing the following genes: none (empty vector) (leaf 1), avrPtoB (leaf 2), avrPtoBT1 (leaf 3), avrPtoBPT23 (leaf 4), avrPtoBB728a (leaf 5), and hopPmaL (leaf 6). Photographs were taken 6 days after inoculation. Disease developed 3 days after inoculation of RG-PtoR leaves with only ΔavrPtoΔavrPtoB(ev) (leaf 1). (C) Bacterial populations in RG-PtoR tomato leaves at 0, 2, and 4 days after inoculation with DC3000ΔavrPtoΔavrPtoB expressing the genes indicated. Leaves were vacuum infiltrated with 104 CFU ml−1 of bacteria. The error bars indicate the standard deviations for three replicates. Data analysis was performed using Duncan's multiple-range test. Means with the same letter above the bars are not different at a significance level of 5%. The experiments were performed twice, and similar results were obtained.