FIG. 7.
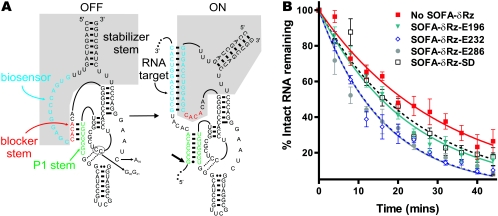
Structure and effect of SOFA-δRz. (A) Secondary structures of the off and on conformations of SOFA-δRz-E232. The shaded area indicates the SOFA module. The P1 stem, the biosensor, and the blocker sequence of the ribozyme are indicated by green, blue, and red, respectively. Upon recognition of its specific target, the biosensor (12 nt) of the SOFA module base pairs 12 nt downstream from the cleavage site. The interaction between the target and the biosensor of the ribozyme disrupts the blocker stem and therefore liberates the substrate recognition sequence of the ribozyme, allowing formation of the P1 stem. The stabilizer stem was designed to mimic the P2 stem in classic δRz, allowing base pairing of both 5′ and 3′ extremities. The small arrow indicates the ribozyme cleavage site. The C76-to-A, C40-to-G, and C41-to-G mutations present in the inactive SOFA-δRz-E232 control are indicated. (B) Graphic representation of EF-Tu mRNA half-lives in the presence of four different SOFA-δRzs.