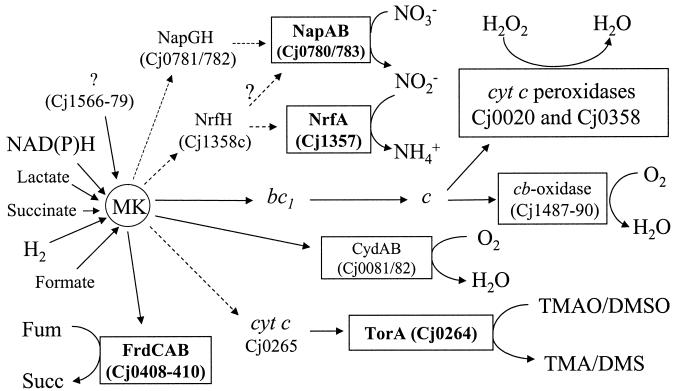
FIG. 1.
Predicted electron transport pathways in C. jejuni. A variety of potential electron donors (not all shown here) feed electrons to the menaquinone pool (MK). Cj1566-79 encodes an Nuo/NdhI-type enzyme which probably does not use NAD(P)H (6, 12, 18). Oxygen-linked respiration occurs via two membrane-bound terminal oxidases, a cytochrome c oxidase and a quinol oxidase. Two unlinked periplasmic cytochrome c peroxidases are also predicted to be reduced by cytochrome c. With the exception of fumarate reductase (FrdCAB), all of the other oxygen-independent terminal reductases are predicted to be periplasmic. Electron transport from quinol to nitrate is more likely to be via the NapGH proteins than the NapC/NrfH homologue (question marks). The molybdoenzyme encoded by Cj0264c is shown in this study to be a TMAO and DMSO reductase with greater activity with TMAO, so it is designated TorA. It probably receives electrons from quinol via a small monoheme c-type cytochrome encoded in the same operon. Fum, fumarate; succ, succinate; bc1, cytochrome bc1 complex. Dashed arrows indicate uncertainty regarding the exact electron transport pathway or the likely participation of additional redox proteins.