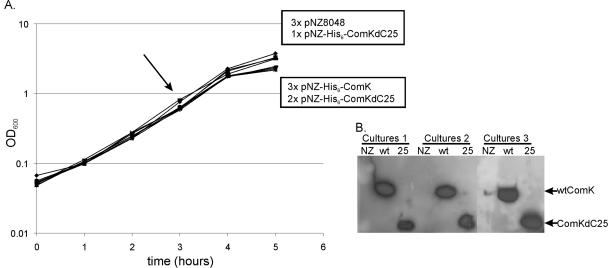
FIG. 2.
Growth and ComK production of the strains tested. (A) Independent cultures of L. lactis NZ9000(pNZ8048), L. lactis NZ9000(pNZ-His6-ComK), and L. lactis NZ9000(pNZ-His6-ComKΔC25) were grown as biological replicates. The moment of induction with supernatant of nisin-producing strain L. lactis NZ9700 at a 1:1,000 dilution is indicated by an arrow. Two growth rates were distinguished after induction of ComK production. For the organisms in the upper box the growth rates of the cultures were normal; for the organisms in the lower box the growth rates of the cultures were decreased. Samples for RNA isolation were harvested after 2 h of induction. OD600, optical density at 600 nm. (B) Western blotting was performed to detect the His-tagged ComK proteins using an anti-His antibody. Samples of three cultures per strain were loaded on a gel. Lanes NZ, L. lactis NZ9000(pNZ8048); lanes wt, L. lactis NZ9000(pNZ-His6-ComK); lanes 25, L. lactis NZ9000(pNZ-His6-ComKΔC25).