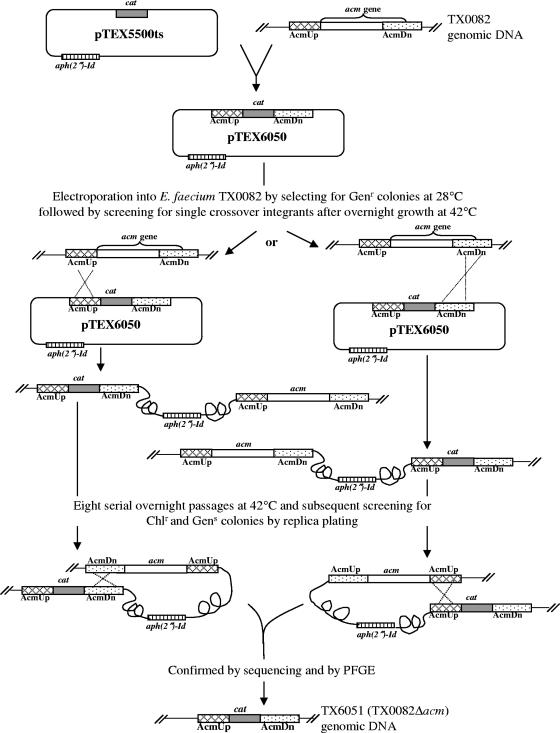
FIG. 2.
Protocol used for replacing the acm wild-type sequence on the TX0082 chromosome with the cat gene. The gene replacement construct (pTEX6050) carrying in vitro-altered sequences (AcmUp, the region upstream of acm [shown by the cross-hatched box], and AcmDn, part of the acm 3′ region as well as the downstream region [shown by the dotted box]) was transformed into E. coli. At permissive temperature (28°C), pTEX6050 was introduced into TX0082 by electroporation. Colonies were screened for an integration event when the temperature was shifted to 42°C. One of the integrants was grown for eight serial overnight passages at 42°C to completely cure the plasmid. The culture from the eighth passage was serially diluted and plated at 37°C on nonselective media to select for double crossover recombination. Upon replica plating to chloramphenicol plates and gentamicin plates, the colonies that retained the cat gene only were identified. One of these colonies was designated TX6051 (TX0082Δacm). The gray box represents the cat gene coding for chloramphenicol resistance, and the striped box represents the aph(2′′)-Id gene coding for gentamicin resistance.