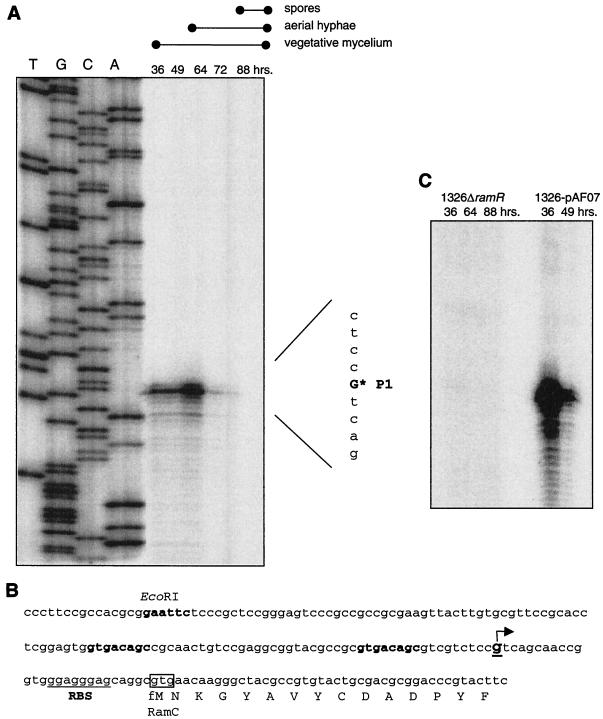
FIG. 4.
Transcription analysis of the ramCSAB operon (A) The transcription start of ramCSAB transcription was analyzed by high-resolution S1 nuclease assay with probe pcp1. This probe encompassed the 5′ end of ramC and upstream regions. The RNA used was isolated at various time points (36, 49, 64, 72, and 88 h) during growth on solid R2YE. The developmental stages are indicated above the panel. The left half of the panel (lanes T, G,C, and A) shows the sequence ladder of the same DNA region that was produced with primer RCRV. The asterisk indicates the transcription start site. (B) Nucleotide sequence of ramC and upstream regions. The arrow indicates the transcription start site that was detected by nuclease S1 mapping. Shown in boldface is a direct repeat overlapping the putative promoter sequence. Underlined is the putative ribosome-binding site (RBS). (C) Transcription of ramC was assessed by nuclease S1 protection assays with pcp1. RNA derived from S. lividans carrying ramR on a high-copy-number vector (1326-pAF07) was isolated after 46 or 49 h of growth corresponding to formation of aerial hyphae. RNA derived from an S. lividans ramR deletion mutant (1326ΔramR) was isolated from cells harvested after 36, 64, or 88 h of growth, during which aerial hyphae (64 h) and spores (88 h) were produced.