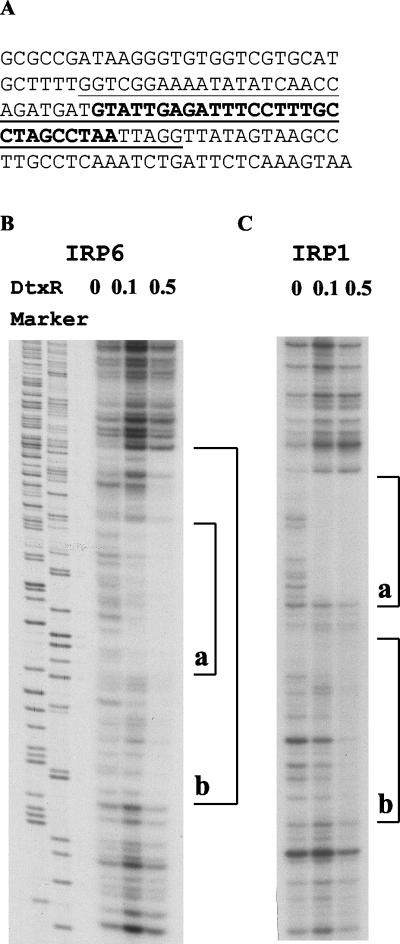
FIG. 2.
(A) Nucleotide sequence of IRP6. The primary DtxR binding site defined by DNase I footprinting assays with DtxR at 0.1 μM is indicated by boldface. The longer nucleotide sequence protected from DNase I by 0.5 μM DtxR is underlined and includes the primary DtxR binding site. (B and C) DNase I footprinting assays. All the fragments were 3′ end labeled with [α-32P]dCTP on one strand and incubated in the presence of Co2+ (300 μM) and DtxR (0, 0.1, or 0.5 μM). Brackets indicate the sequences protected by DtxR from DNase I digestion. (B) With IRP6, a longer 60-bp sequence (b) was protected by 0.5 μM DtxR and a shorter 28-bp sequence (a) that is contained within sequence b was significantly protected by 0.1 μM DtxR. Although the total radioactivity loaded in the lane with 0.1 μM DtxR was greater than that in the other lanes, the intensity of the bands within the 28-bp (a) sequence was decreased significantly both in comparison withbands in other regions of the same lane and with bands in the same 28-bp region in the lane without DtxR. (C) In IRP1, two contiguous regions (a and b) were protected by 0.5 μM DtxR but only region a was protected by 0.1 μM DtxR.