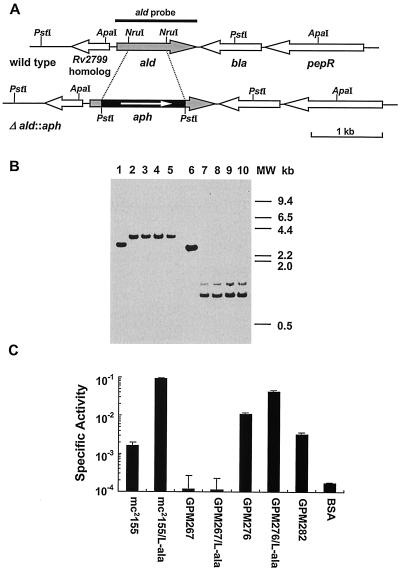
FIG. 4.
Construction and characterization of M. smegmatis ald null mutants. (A) Open reading frame organization at the ald locus in both strain mc2155 (wild type) and the ald null mutant strain (Δald::aph). Relevant restriction enzyme sites and the PCR fragment used as the ald probe are indicated. (B) Southern blot analysis of genomic DNA from wild-type and ald null mutant strains. Genomic DNA was digested with ApaI (lanes 1 to 5) or PstI (lanes 6 to 10). The strains examined are wild-type strain mc2155 (lanes 1 and 6) and ald mutants GPM267 (lanes 2 and 7), GPM268 (lanes 3 and 8), GPM269 (lanes 4 and 9), and GPM270 (lanes 5 and 10). Blots were hybridized with the radiolabeled 1.1-kb PCR fragment containing the ald gene and washed under stringent conditions as described in Materials and Methods. MW, molecular weight. (C) Analysis of l-alanine dehydrogenase activities in M. smegmatis wild-type, mutant, and recombinant strains. Extracts from organisms grown in both M-ADC-TW and M-ADC-TW supplemented with l-alanine were prepared and analyzed. Ald specific activities are expressed in micromoles of l-alanine per milligram per minute. The values are means ± standard deviations of triplicate measurements. A mock assay was also carried out with bovine serum albumin (BSA) in place of equivalent amounts of the cell extracts.