Abstract
1. A study has been made of the effects of changing the external calcium concentration [Ca]o on the binomial parameters p and n that control the average quantal content (m̄) of the end-plate potential (e.p.p.) during trains of nerve impulses at synapses in amphibian striated muscle.
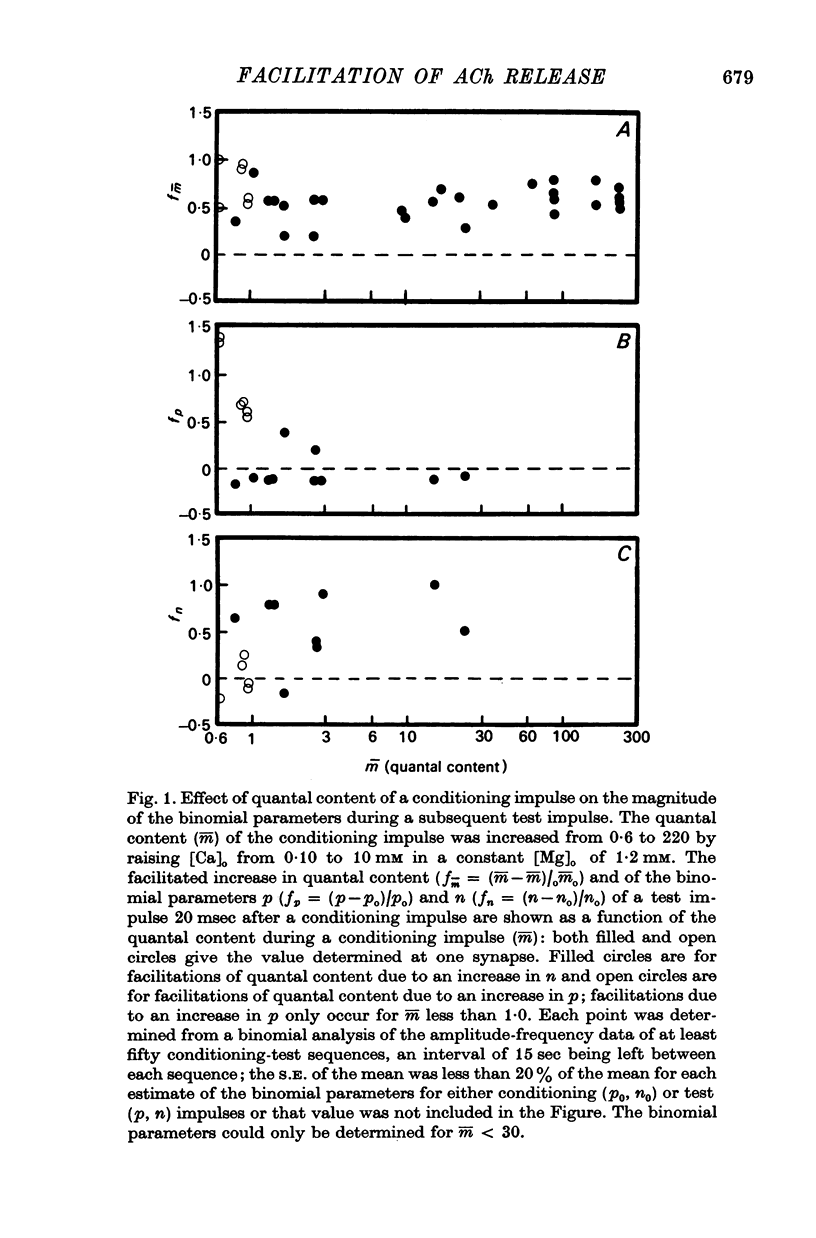
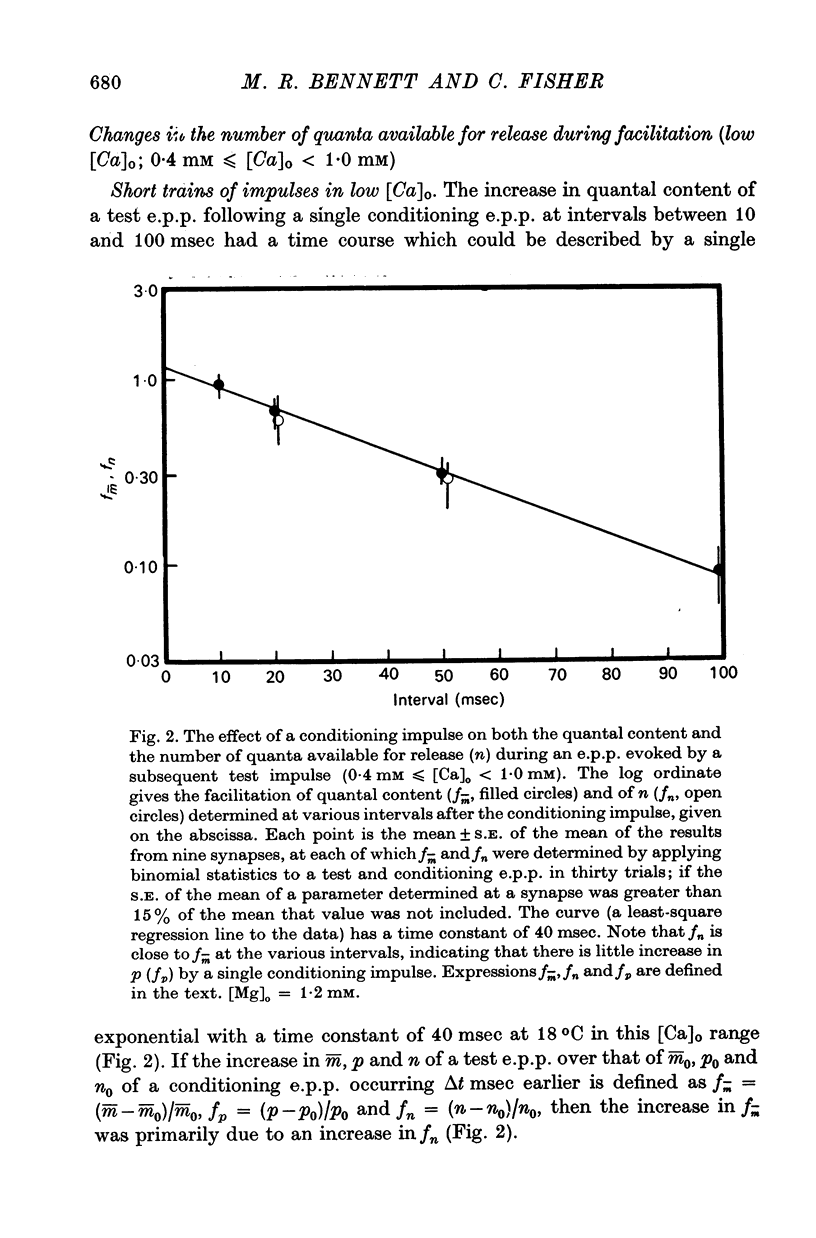
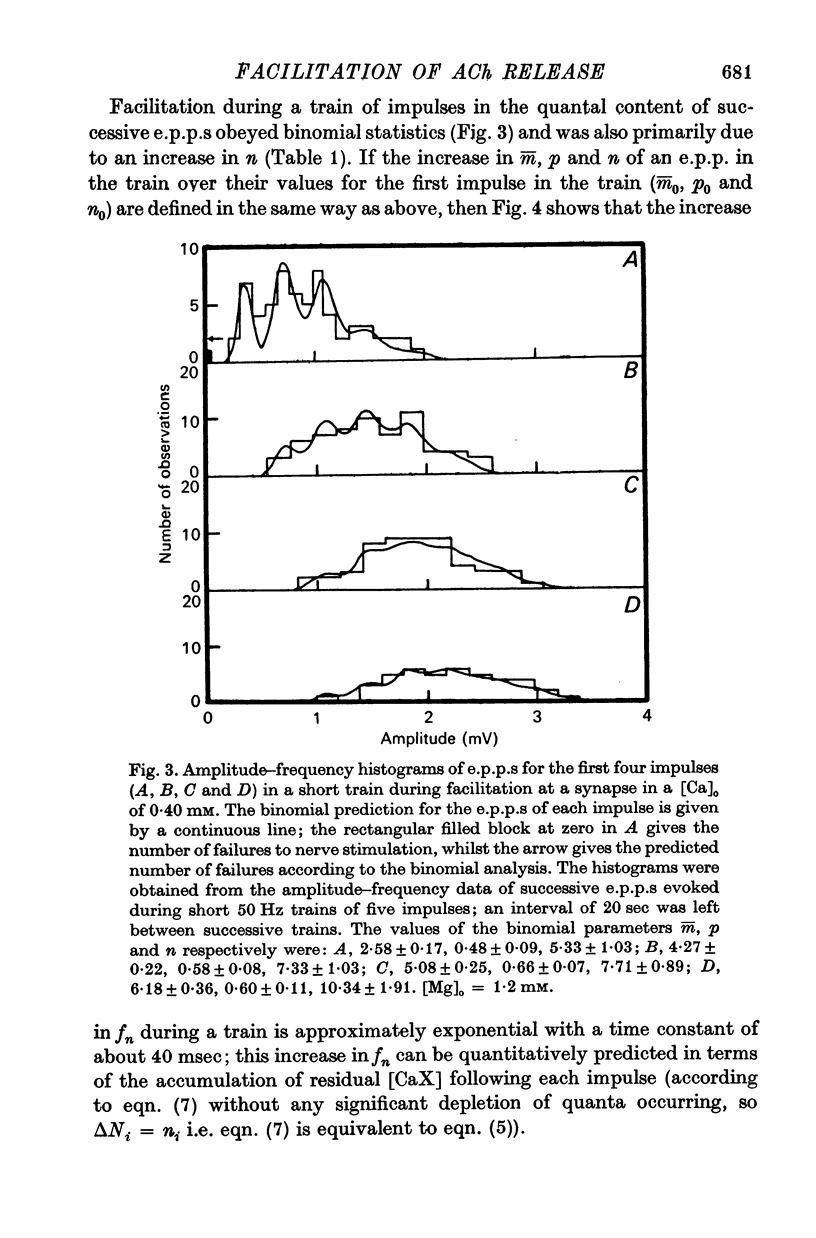
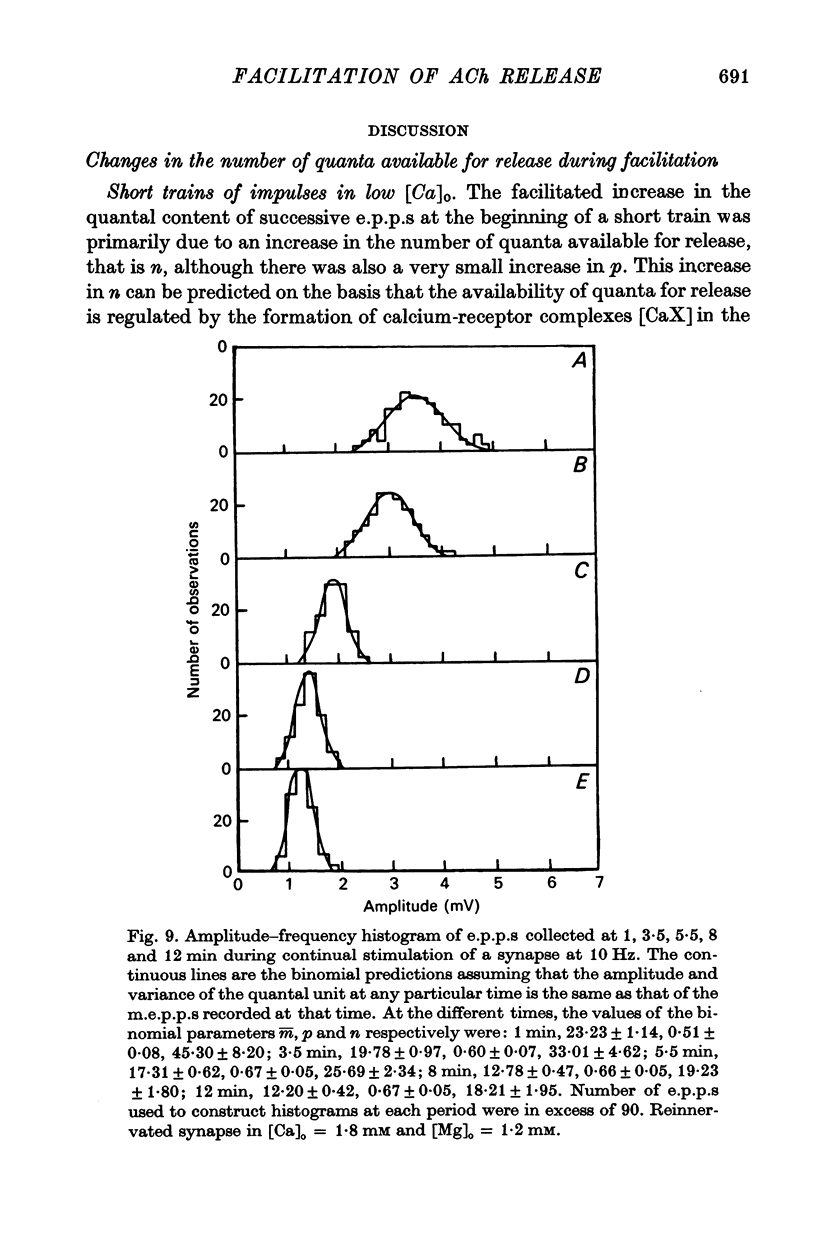
2. In high external calcium concentrations (0·4 mM ≤ [Ca]o < 1·0 mM) the increase in m̄ of a test impulse following a conditioning impulse at different intervals (< 100 msec) was due to an increase in the number of quanta available for release, n; the increase in m̄ of successive e.p.p.s in a short high frequency train was primarily due to an increase in n.
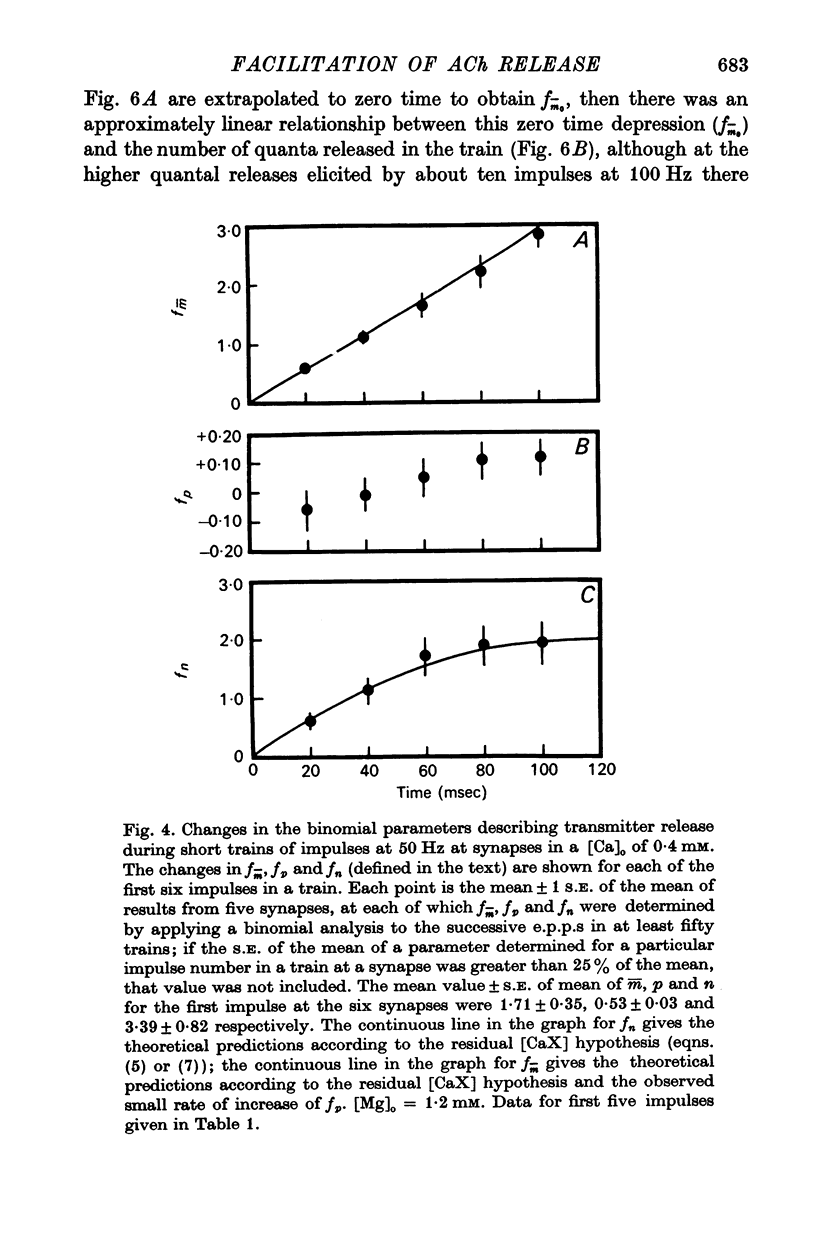
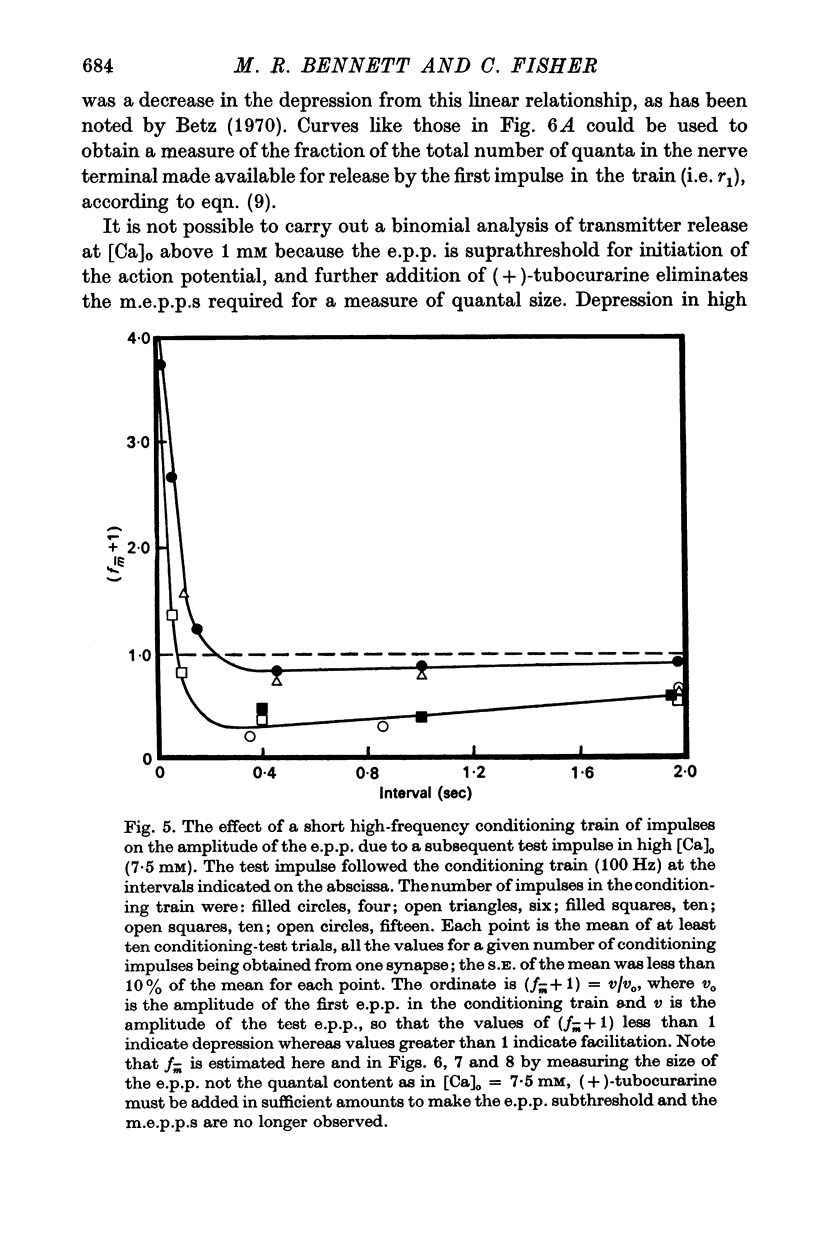
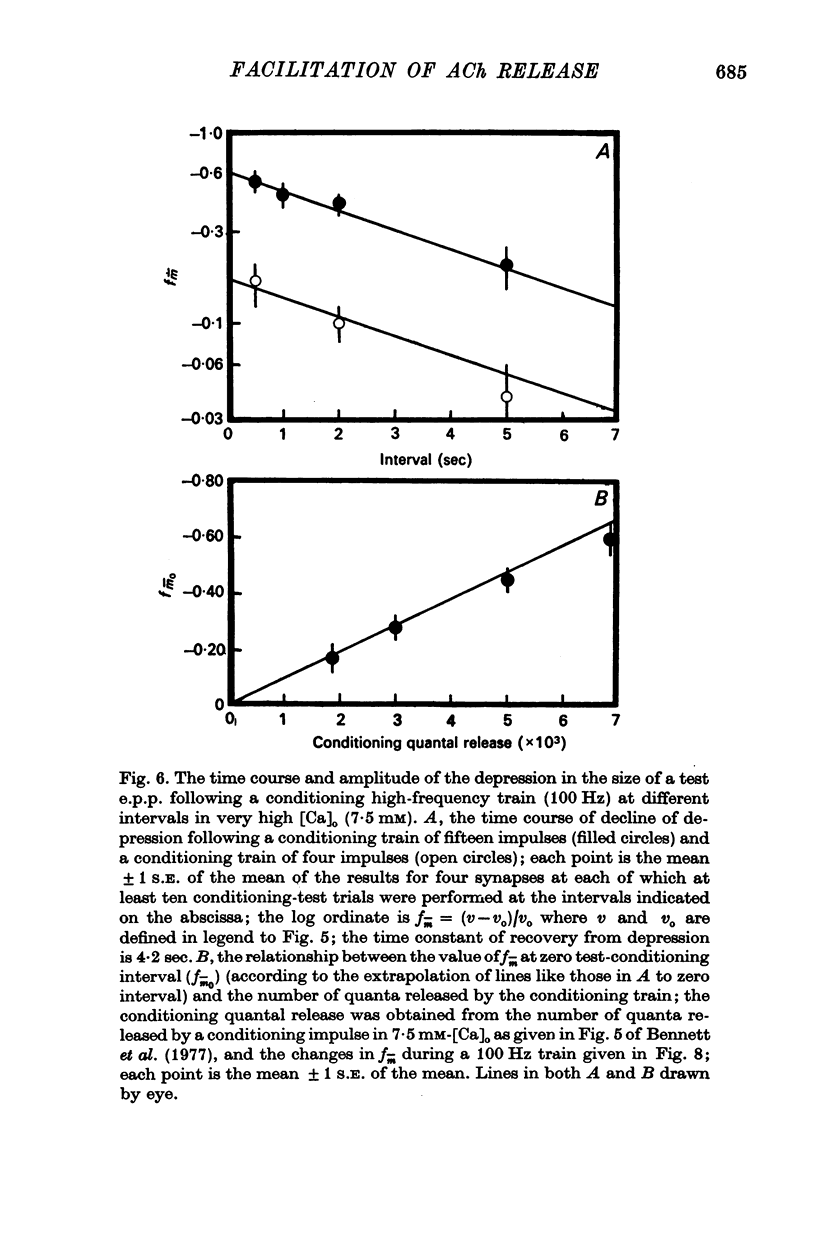
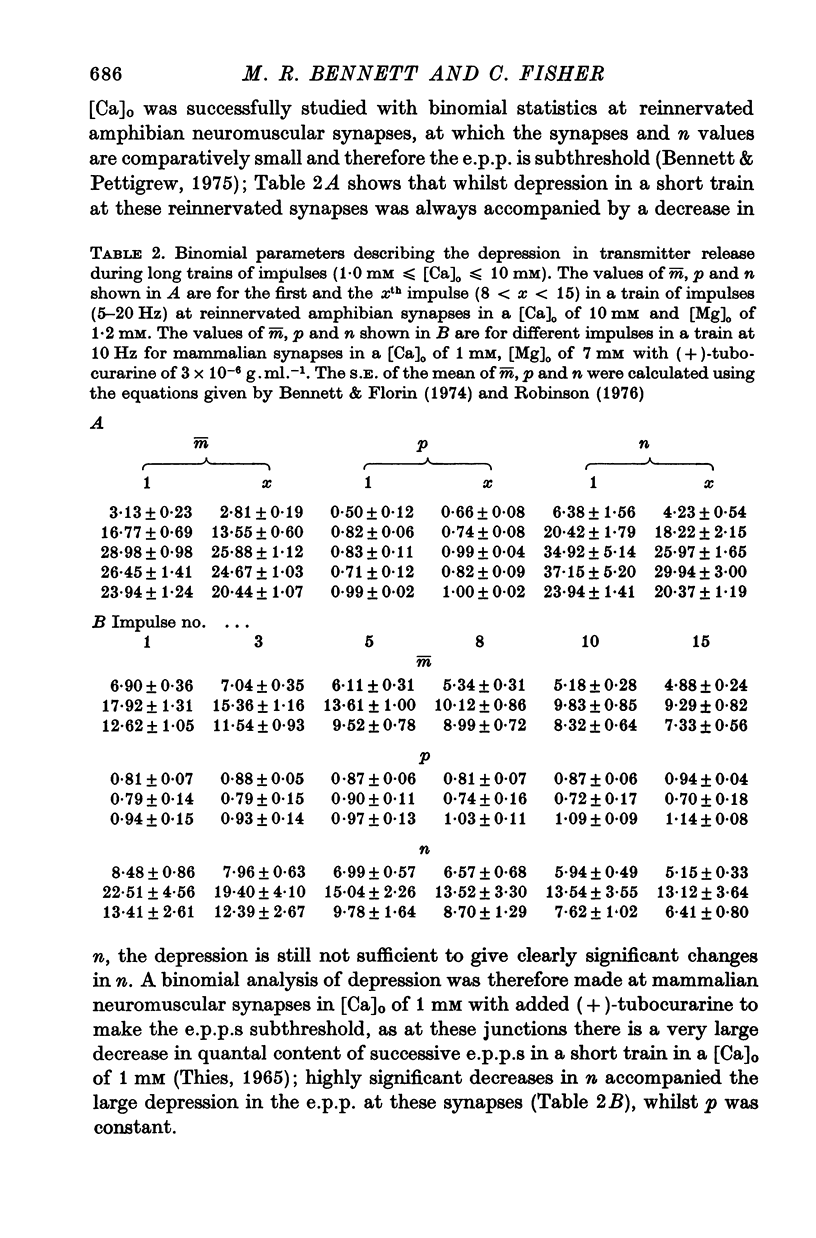
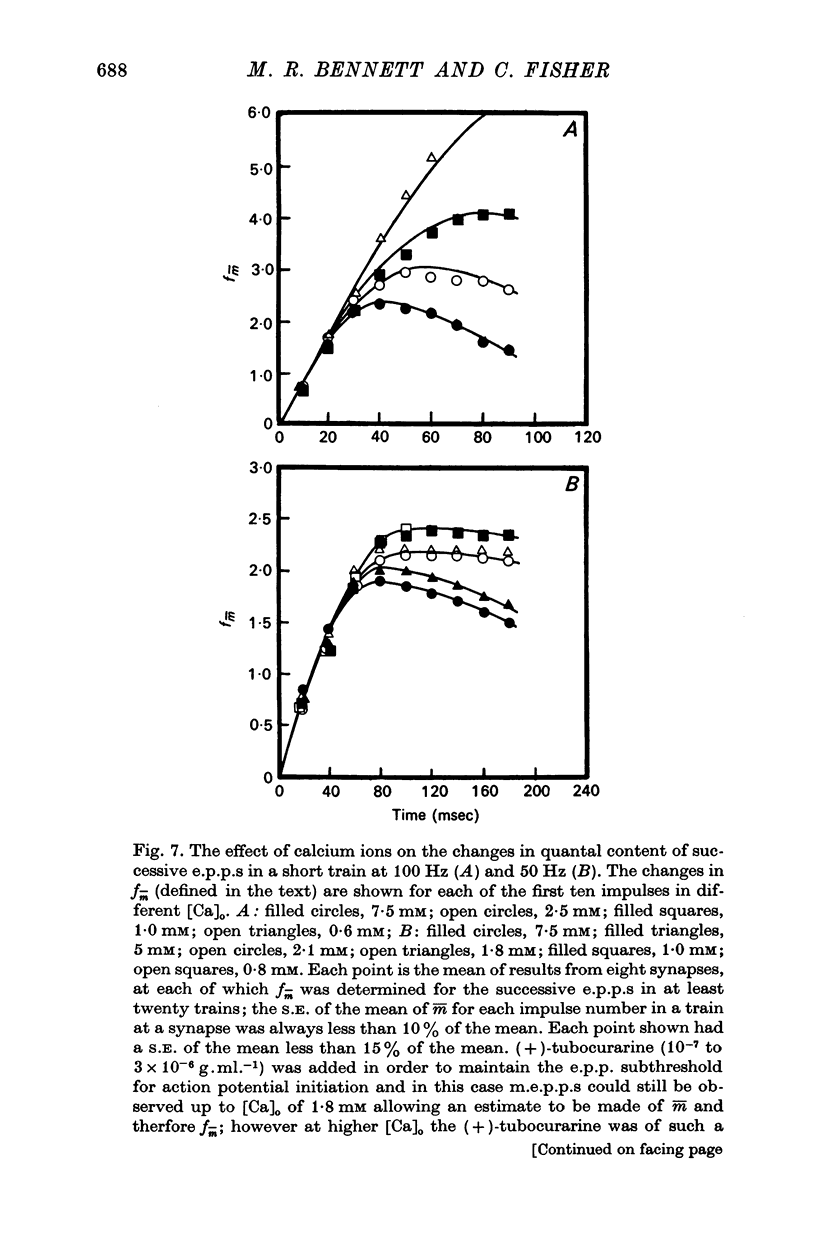
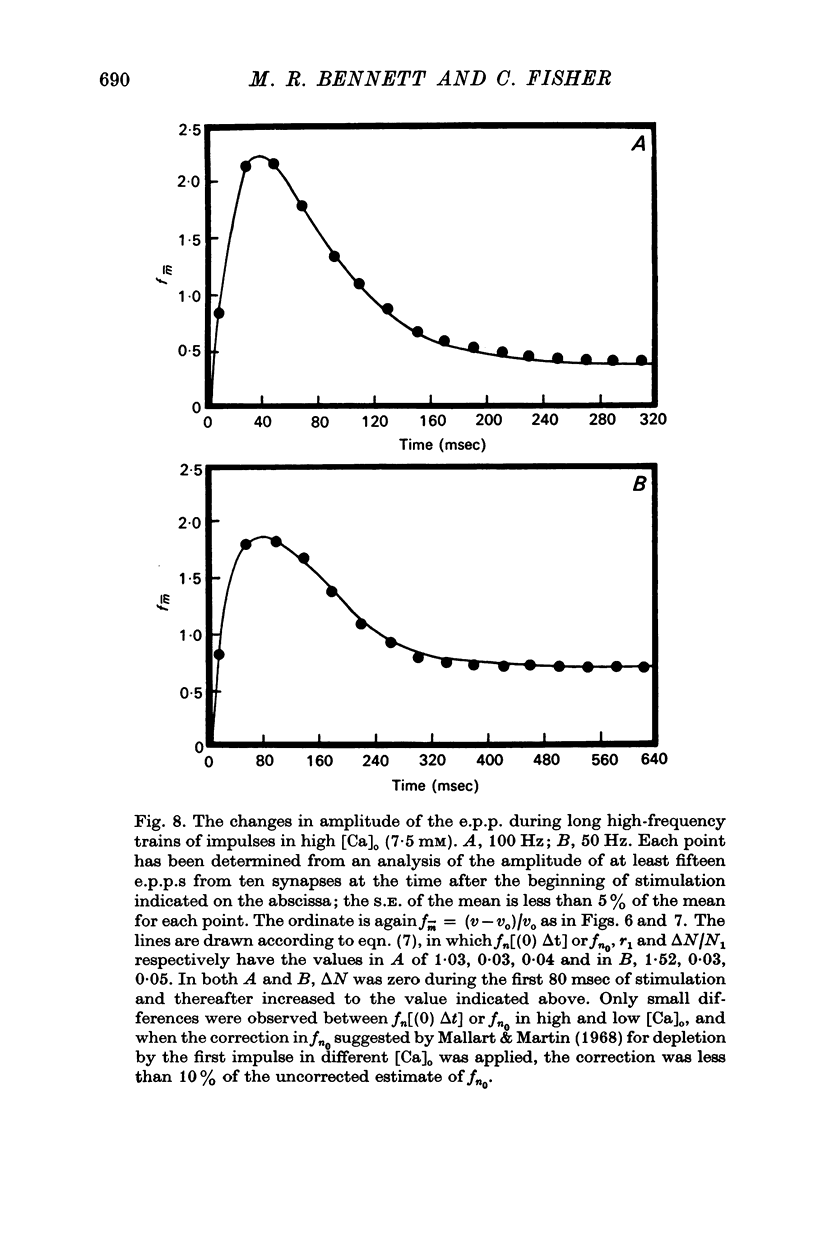
3. In high external calcium concentrations (1·0 mM ≤ [Ca]o < 10 mM) there was a decrease in m̄ of a test impulse following a short high frequency conditioning train (4-5 impulses, 20-100 Hz) at different intervals (200 msec < 5 sec) and this was due to a decrease in the number of quanta available for release, n; in a long high frequency train (20 impulses, 20-100 Hz) there was an increase in m̄ for the first few successive e.p.p.s followed by a depression of m̄ which eventually reached a steady state and these changes in m̄ were due to changes in n; the higher the frequency the greater was the depression in n during the steady-state period.
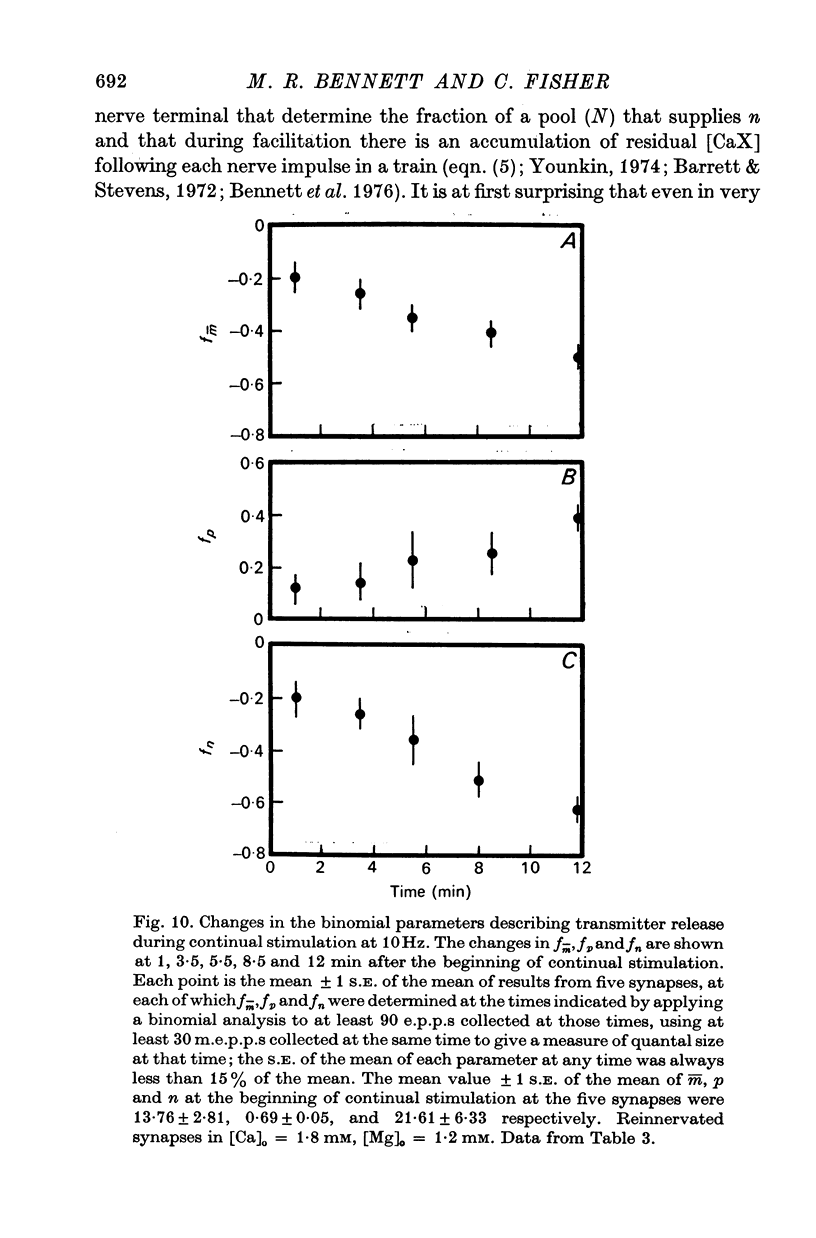
4. In high calcium concentrations, the steady-state m̄ reached in the first 20 impulses during continual stimulation at high frequency gave way to a decline in m̄ over several minutes until a new depressed steady-state value of m̄ was reached and this was maintained during the longest periods of stimulation (30 min); this decline in m̄ was primarily due to a decline in the number of quanta available for release.
5. These changes in the number of quanta available for release during trains of impulses are predicted in terms of a hypothesis in which facilitation is due to the accumulation of a residual calcium-receptor complex in the nerve terminal that determines the fraction of a pool of quanta which contributes to n, and depression is due to a decrease in the number of quanta in this pool.
Full text
PDF














Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker P. F., Hodgkin A. L., Ridgway E. B. Depolarization and calcium entry in squid giant axons. J Physiol. 1971 Nov;218(3):709–755. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett E. F., Stevens C. F. The kinetics of transmitter release at the frog neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1972 Dec;227(3):691–708. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp010054. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett M. R., Fisher C., Florin T., Quine M., Robinson J. The effect of calcium ions and temperature on the binomial parameters that control acetylcholine release by a nerve impulse at amphibian neuromuscular synapses. J Physiol. 1977 Oct;271(3):641–672. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp012019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett M. R., Florin T. A statistical analysis of the release of acetylcholine at newly formed synapses in striated muscle. J Physiol. 1974 Apr;238(1):93–107. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010512. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett M. R., Florin T., Hall R. The effect of calcium ions on the binomial statistic parameters which control acetylcholine release at synapses in striated muscle. J Physiol. 1975 May;247(2):429–446. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp010939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett M. R., Florin T., Pettigrew A. G. The effect of calcium ions on the binomial statistic parameters that control acetylcholine release at preganglionic nerve terminals. J Physiol. 1976 Jun;257(3):597–620. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett M. R., McLachlan E. M. An electrophysiological analysis of the storage of acetylcholine in preganglionic nerve terminals. J Physiol. 1972 Mar;221(3):657–668. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009774. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett M. R., McLachlan E. M. An electrophysiological analysis of the synthesis of acetylcholine in preganglionic nerve terminals. J Physiol. 1972 Mar;221(3):669–682. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009775. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett M. R., Pettigrew A. G. The formation of synapses in amphibian striated muscle during development. J Physiol. 1975 Oct;252(1):203–239. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Betz W. J. Depression of transmitter release at the neuromuscular junction of the frog. J Physiol. 1970 Mar;206(3):629–644. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown T. H., Perkel D. H., Feldman M. W. Evoked neurotransmitter release: statistical effects of nonuniformity and nonstationarity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Aug;73(8):2913–2917. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.8.2913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodge F. A., Jr, Rahamimoff R. Co-operative action a calcium ions in transmitter release at the neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1967 Nov;193(2):419–432. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elmqvist D., Quastel D. M. A quantitative study of end-plate potentials in isolated human muscle. J Physiol. 1965 Jun;178(3):505–529. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1965.sp007639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., KEYNES R. D. Movements of labelled calcium in squid giant axons. J Physiol. 1957 Sep 30;138(2):253–281. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005850. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartzell H. C., Kuffler S. W., Yoshikami D. Post-synaptic potentiation: interaction between quanta of acetylcholine at the skeletal neuromuscular synapse. J Physiol. 1975 Oct;251(2):427–463. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatt H., Smith D. O. Synaptic depression related to presynaptic axon conduction block. J Physiol. 1976 Jul;259(2):367–393. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LILEY A. W., NORTH K. A. An electrical investigation of effects of repetitive stimulation on mammalian neuromuscular junction. J Neurophysiol. 1953 Sep;16(5):509–527. doi: 10.1152/jn.1953.16.5.509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linder T. M. Calcium and facilitation at two classes of crustacean neuromuscular synapses. J Gen Physiol. 1973 Jan;61(1):56–73. doi: 10.1085/jgp.61.1.56. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magleby K. L. The effect of repetitive stimulation on facilitation of transmitter release at the frog neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1973 Oct;234(2):327–352. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010348. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mallart A., Martin A. R. An analysis of facilitation of transmitter release at the neuromuscular junction of the frog. J Physiol. 1967 Dec;193(3):679–694. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008388. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mallart A., Martin A. R. The relation between quantum content and facilitation at the neuromuscular junction of the frog. J Physiol. 1968 Jun;196(3):593–604. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson J. Estimation of parameters for a model of transmitter release at synapses. Biometrics. 1976 Mar;32(1):61–68. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stinnakre J., Tauc L. Calcium influx in active Aplysia neurones detected by injected aequorin. Nat New Biol. 1973 Mar 28;242(117):113–115. doi: 10.1038/newbio242113b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAKEUCHI A. The long-lasting depression in neuromuscular transmission of frog. Jpn J Physiol. 1958 Jun 15;8(2):102–113. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.8.102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THIES R. E. NEUROMUSCULAR DEPRESSION AND THE APPARENT DEPLETION OF TRANSMITTER IN MAMMALIAN MUSCLE. J Neurophysiol. 1965 May;28:428–442. doi: 10.1152/jn.1965.28.3.427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinreich D. Ionic mechanism of post-tetanic potentiation at the neuromuscular junction of the frog. J Physiol. 1971 Jan;212(2):431–446. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


