Abstract
1. An anatomical basis was sought for the biphasic motor nerve response of the rat vas deferens. The motor nerve pathway to the tissue was stimulated at different points between the vertebral outflow and the intramural fibres, in the pithed rat and in isolated tissues, to examine the possibility of two anatomically separate groups of neurones. Different preparations of the isolated tissue were devised to detect whether different groups of smooth muscle fibres contributed to the two phases.
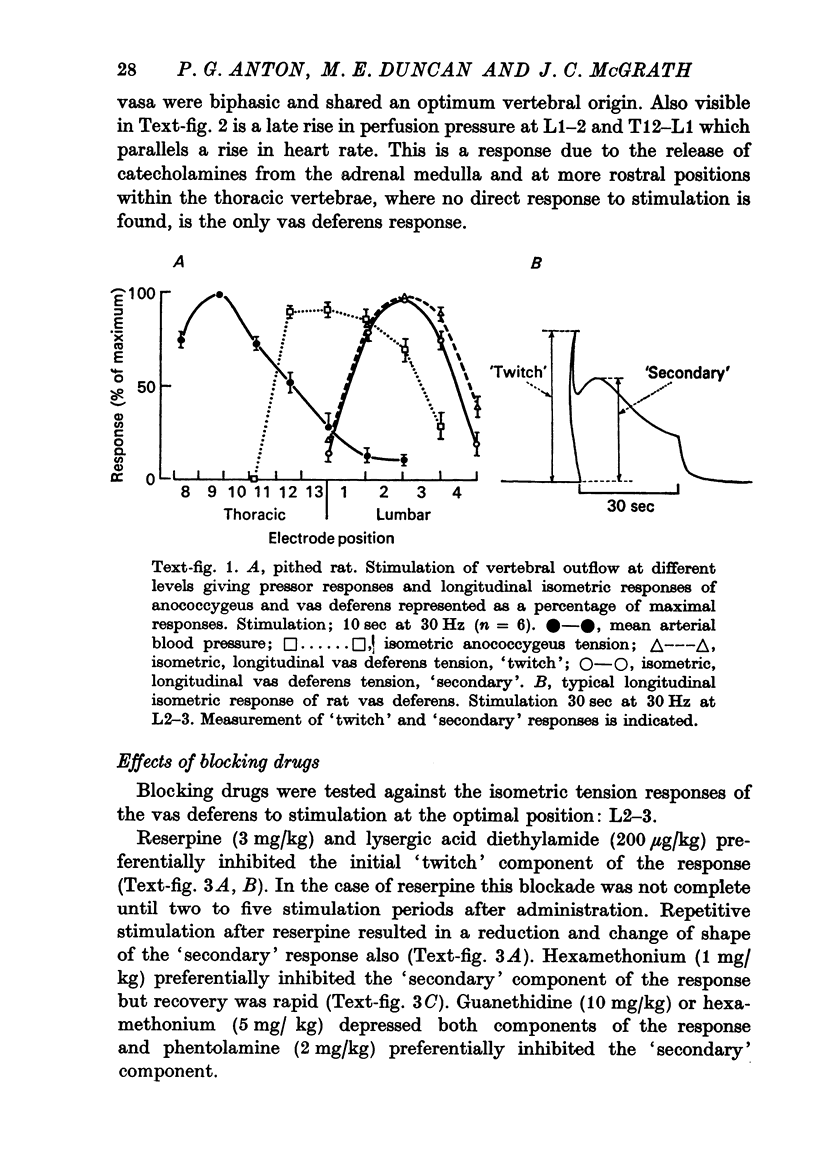
2. The fibres mediating both phases of the response arose from the upper lumbar vertebral outflows. Both phases were elicited by pre- or post-ganglionic stimulation and could be depressed by hexamethonium. In the pithed rat or with hypogastric nerve stimulation in the isolated tissue, however, the initial `twitch' phase was relatively resistant to such blockade.
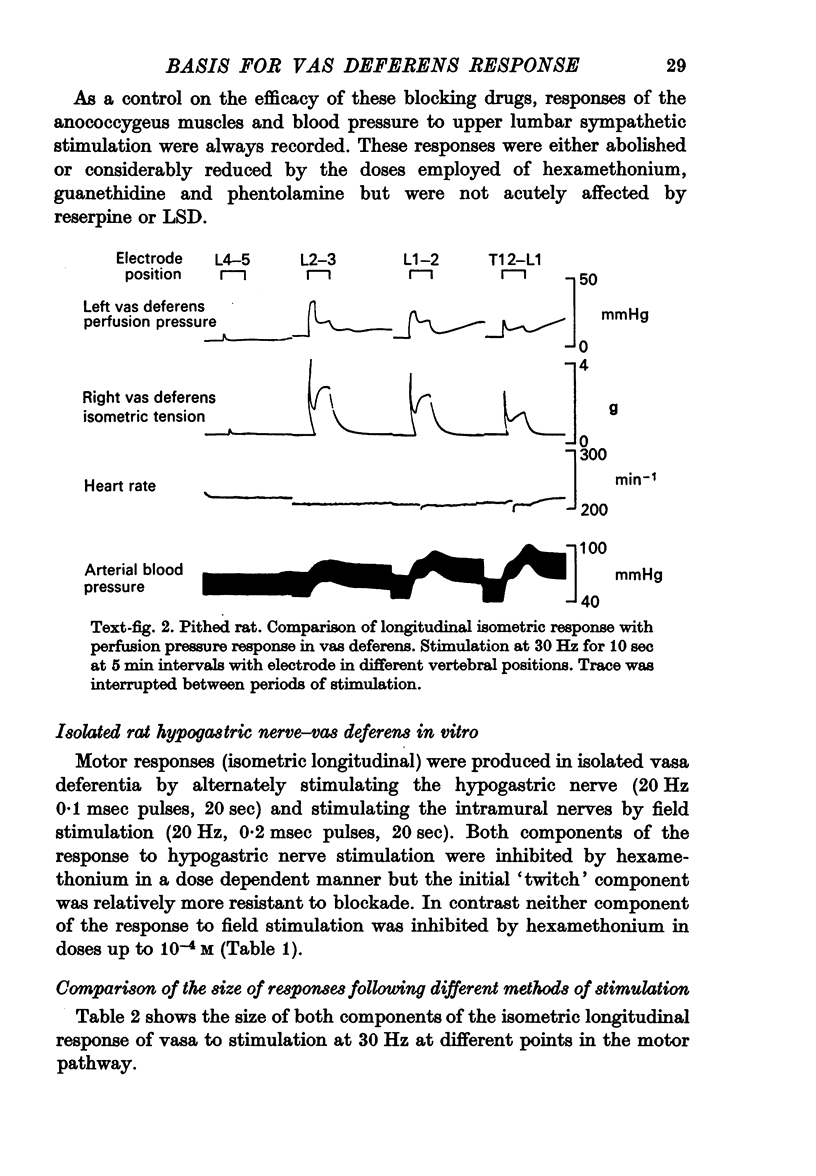
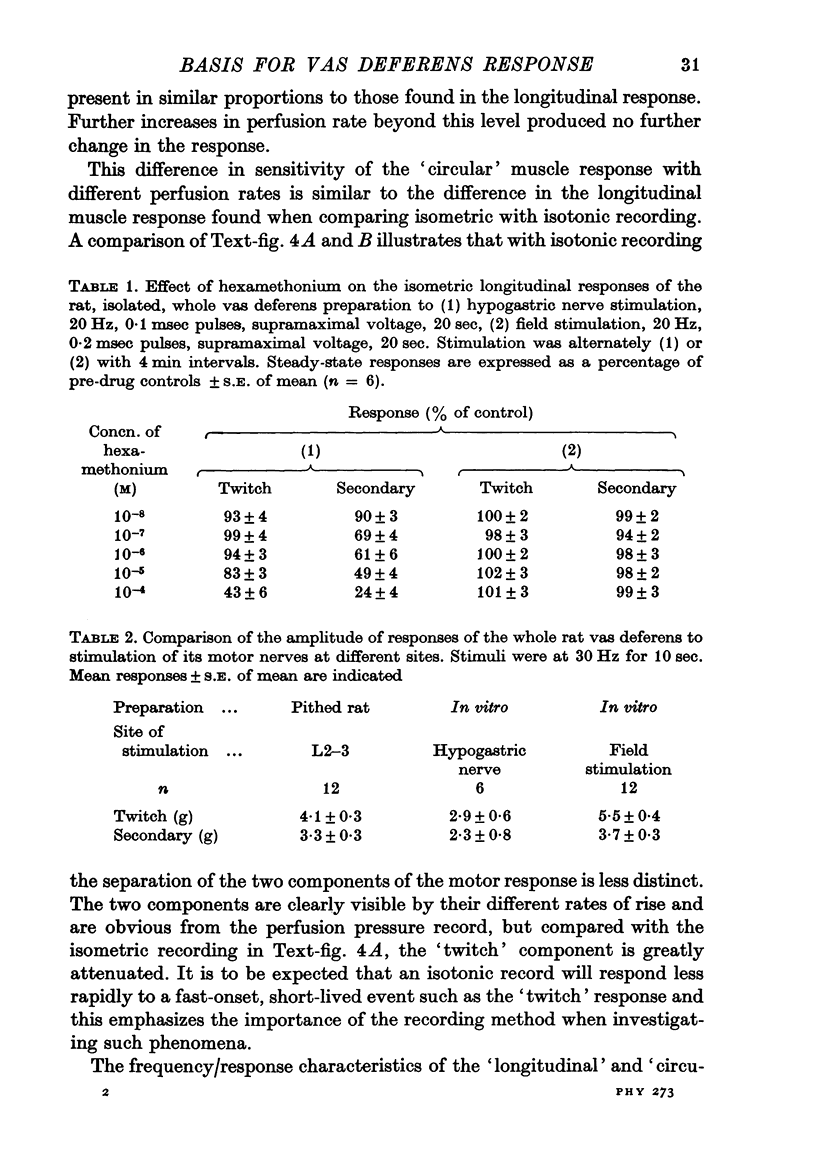
3. When the rat vas deferens was perfused through the lumen in situ or in vitro, the perfusion pressure response to motor nerve stimulation exhibited two phases similar to those of the longitudinal contractile response.
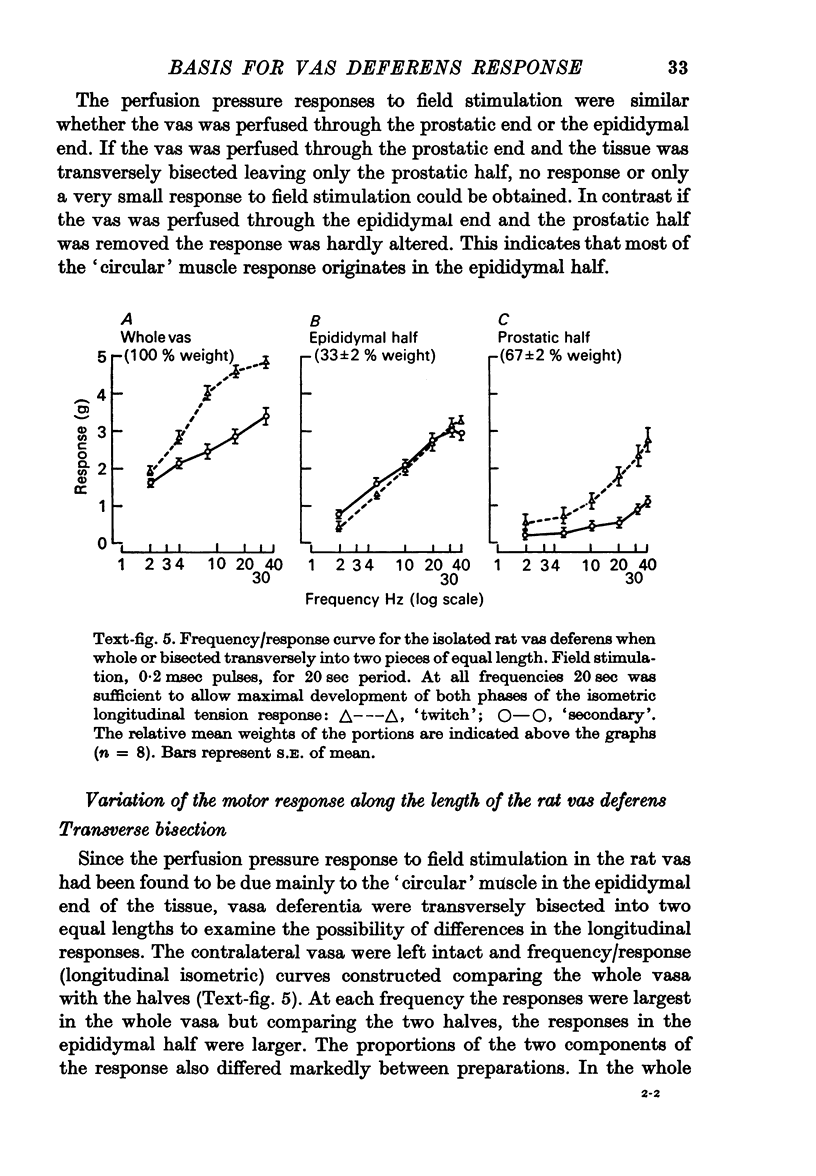
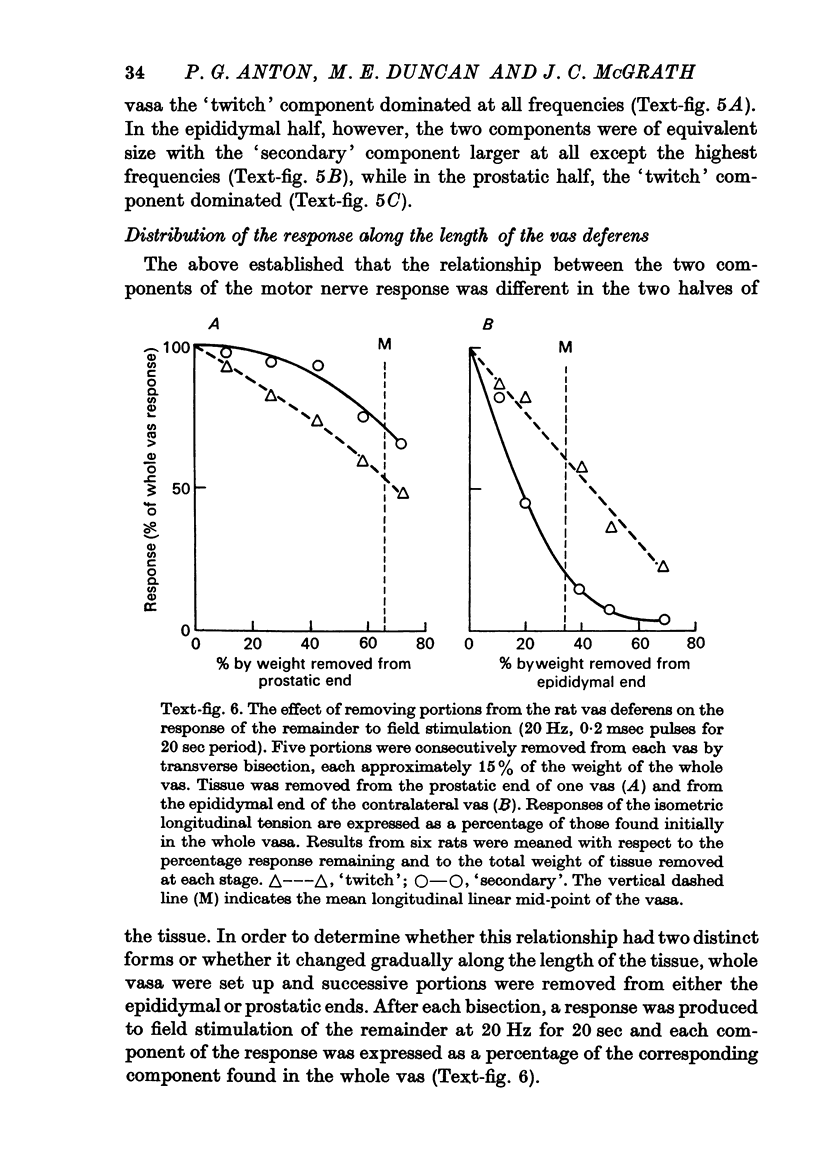
4. Isolated rat vasa were bisected into portions, each of which was stimulated and longitudinal tension was recorded. The proportions of the two phases of the response varied along the length of the tissue. At the prostatic end the total response was relatively weak with a dominant `twitch' and at the epididymal end the two phases were comparable in magnitude. The distribution of adrenergic nerve terminals within the muscle layers also varied along the length of the rat vas deferens.
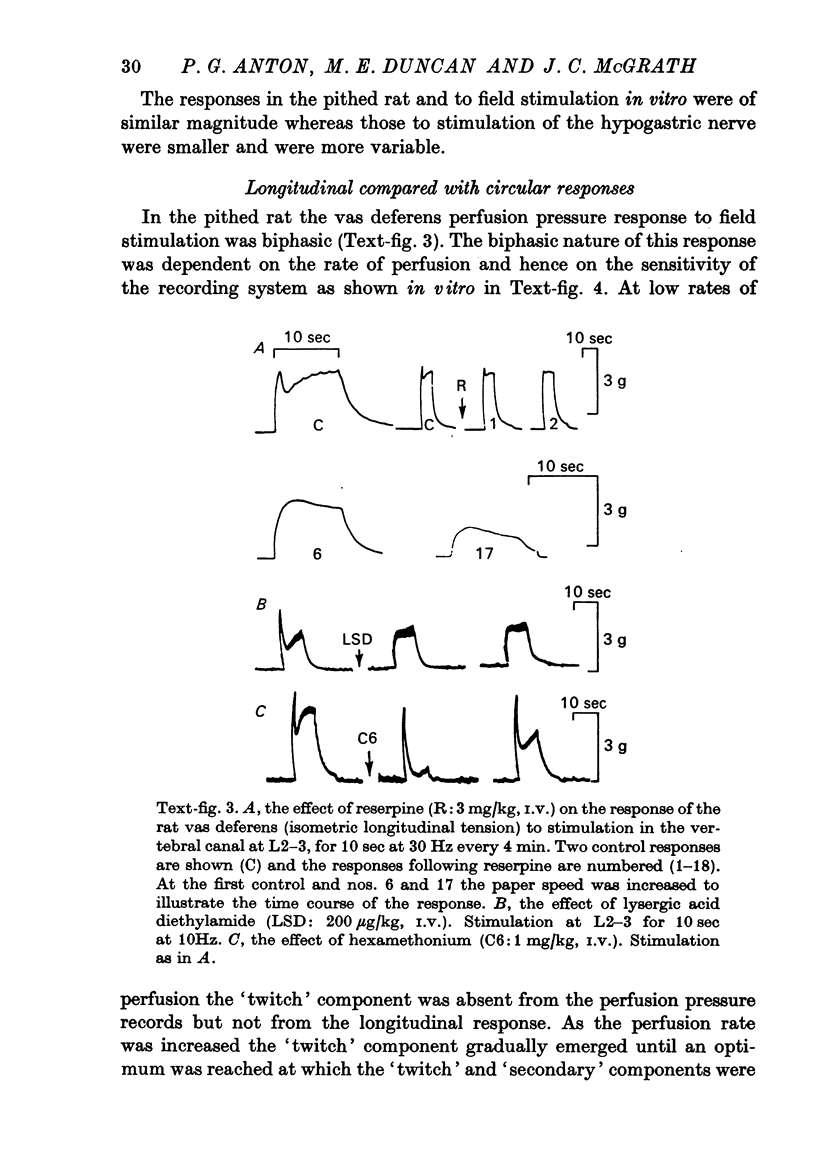
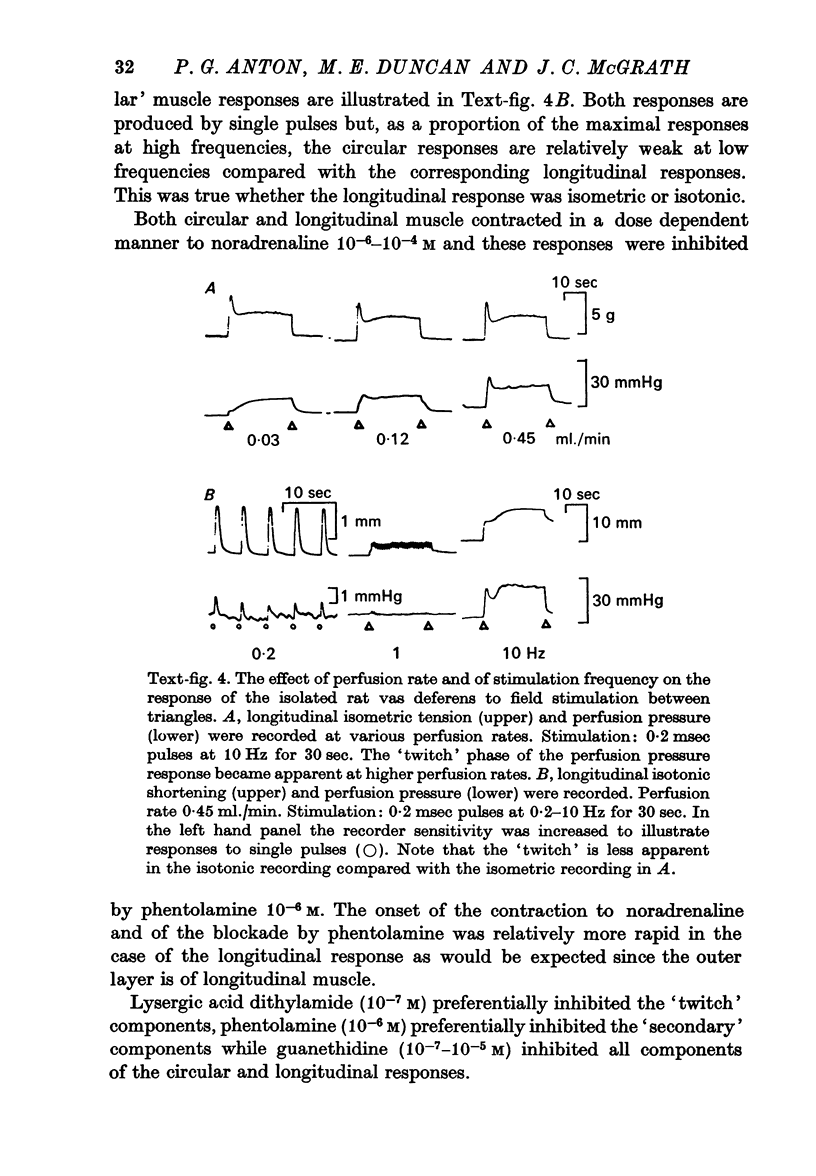
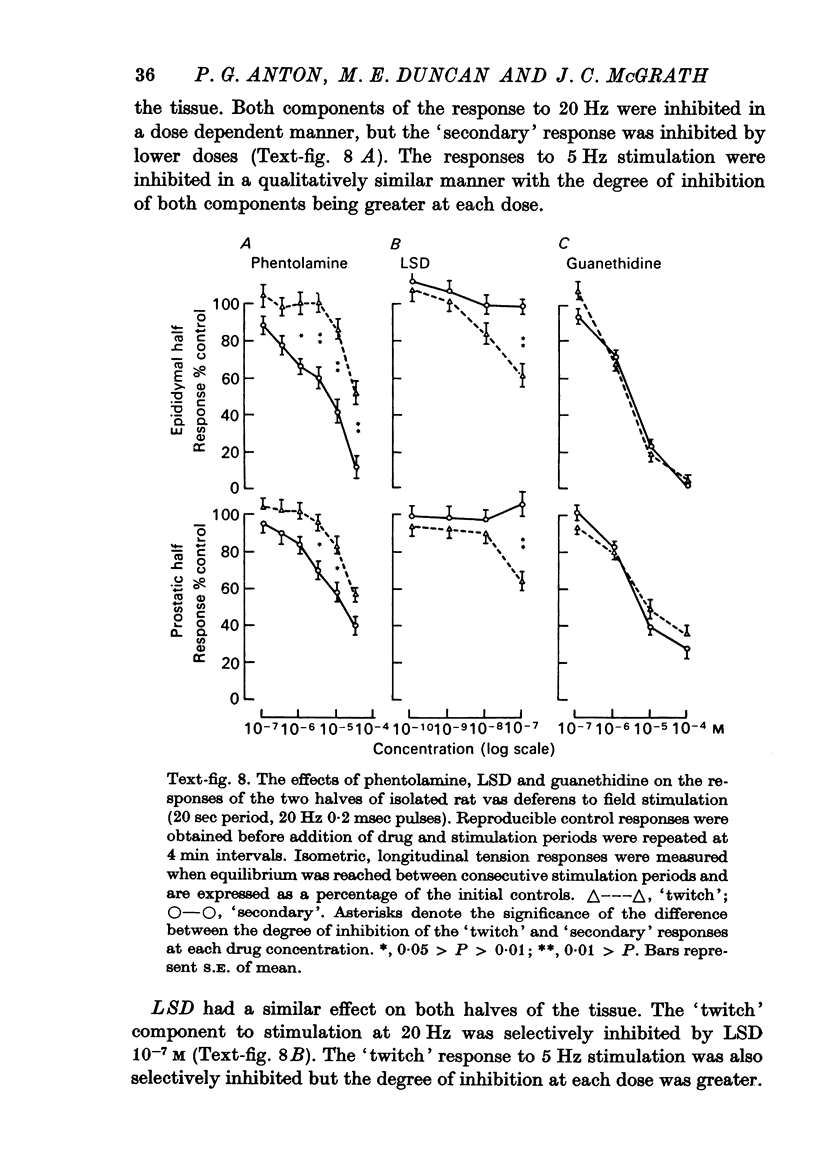
5. The effects of drugs were investigated on the motor responses of the above preparations. The `twitch' phase was relatively susceptible to blockade by reserpine and lysergic acid diethylamide and the `secondary' phase to phentolamine with both equally sensitive to guanethidine. Each phase had similar susceptibilities to blockade irrespective of which part of the tissue was involved.
6. It was concluded that two types of nerve-muscle transmission may be involved in the rat vas deferens with the proportion of each varying along the length of the tissue but both displaying pharmacological characteristics of adrenergic fibres.
Full text
PDF












Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ambache N., Dunk L. P., Verney J., Zar M. A. Inhibition of post-ganglionic motor transmission in vas deferens by indirectly acting sympathomimetic drugs. J Physiol. 1972 Dec;227(2):433–456. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp010041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anton P. G., McGrath J. C. Further evidence for adrenergic transmission in the human vas deferens. J Physiol. 1977 Dec;273(1):45–55. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp012080. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BENTLEY G. A., SABINE J. R. THE EFFECTS OF GANGLION-BLOCKING AND POSTGANGLIONIC SYMPATHOLYTIC DRUGS ON PREPARATIONS OF THE GUINEA-PIG VAS DEFERENS. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1963 Aug;21:190–201. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1963.tb01515.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BIRMINGHAM A. T., WILSON A. B. PREGANGLIONIC AND POSTGANGLIONIC STIMULATION OF THE GUINEA-PIG ISOLATED VAS DEFERENS PREPARATION. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1963 Dec;21:569–580. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1963.tb02024.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birmingham A. T., Freeman M. A. The relation between stimulus frequency and the relative size of the components of the biphasic response of the vas deferens to electrical stimulation at different temperatures. J Physiol. 1976 Apr;256(3):747–759. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHANG C. C., COSTA E., BRODIE B. B. INTERACTION OF GUANETHIDINE WITH ADRENERGIC NEURONS. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1965 Mar;147:303–312. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang C. C., Chang J. C., Su C. Y. Studies on the interactions of guanethidine and bretylium with noradrenaline stores. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1967 Jun;30(2):213–223. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1967.tb02127.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DIXIT B. N., GULATI O. D., GOKHALE S. D. Action of bretylium and guanethidine at the neuromuscular junction. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1961 Dec;17:372–379. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1961.tb01123.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon J. S., Gosling J. A. The distribution of autonomic nerves in the musculature of the rat vas deferens. A light and electron microscope investigation. J Comp Neurol. 1972 Oct;146(2):175–188. doi: 10.1002/cne.901460204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan M. E., McGrath J. C. Proceedings: Observations on the origin of the complex mechanical response to motor nerve stimulation of the rat vas deferens. J Physiol. 1976 Jul;259(1):54P–55P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferry C. B. The innervation of the vas deferens of the guinea-pig. J Physiol. 1967 Sep;192(2):463–478. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillespie J. S., Kirpekar S. M. The histological localization of noradrenaline in the cat spleen. J Physiol. 1966 Nov;187(1):69–79. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1966.sp008076. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillespie J. S., Maclaren A., Pollock D. A method of stimulating different segments of the autonomic outflow from the spinal column to various organs in the pithed cat and rat. Br J Pharmacol. 1970 Oct;40(2):257–267. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1970.tb09919.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillespie J. S., McGrath J. C. The effect of pithing and of nerve stimulation on the depletion of noradrenaline by reserpine in the rat anococcygeus muscle and vas deferens. Br J Pharmacol. 1974 Dec;52(4):585–590. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1974.tb09727.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillespie J. S., McGrath J. C. The effects of lysergic acid diethylamide on the response to field stimulation of the rat vas deferens and the rat and cat anococcygeus muscles. Br J Pharmacol. 1975 Aug;54(4):481–488. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1975.tb07594.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillespie J. S., McGrath J. C. The spinal origin of the motor and inhibitory innervation of the rat anococcygeus muscles. J Physiol. 1973 May;230(3):659–672. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham J. D., al Katib H., Spriggs T. L. The isolated hypogastric nerve-vas deferens preparation of the rat. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1968 Jan;32(1):34–45. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1968.tb00427.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HERTZLER E. C. 5-Hydroxytryptamine and transmission in sympathetic ganglia. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1961 Dec;17:406–413. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1961.tb01126.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes J. Evaluation of mechanisms controlling the release and inactivation of the adrenergic transmitter in the rabbit portal vein and vas deferens. Br J Pharmacol. 1972 Mar;44(3):472–491. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1972.tb07285.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes J. Inhibition of noradrenaline release by lysergic acid diethylamide. Br J Pharmacol. 1973 Dec;49(4):706–708. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1973.tb08549.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KURIYAMA H. ELECTROPHYSIOLOGICAL OBSERVATIONS ON THE MOTOR INNERVATION OF THE SMOOTH MUSCLE CELLS IN THE GUINEA-PIG VAS DEFERENS. J Physiol. 1963 Nov;169:213–228. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PATON W. D. M., ZAIMIS E. J. Paralysis of autonomic ganglia by methonium salts. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1951 Mar;6(1):155–168. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1951.tb00631.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stjärne L. Prostaglandin-versus alpha-adrenoceptor-mediated control of sympathetic neurotransmitter secretion in guinea-pig isolated vas deferens. Eur J Pharmacol. 1973 Jun;22(3):233–238. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(73)90021-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Euler U. S. Acute neuromuscular transmission failure in vas deferens after reserpine. Acta Physiol Scand. 1969 May-Jun;76(1):255–256. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1969.tb04468.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Euler U. S., Hedqvist P. Inhibitory action of prostaglandins E1 and E2 on the neuromuscular transmission in the guinea pig vas deferens. Acta Physiol Scand. 1969 Dec;77(4):510–512. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1969.tb04593.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]