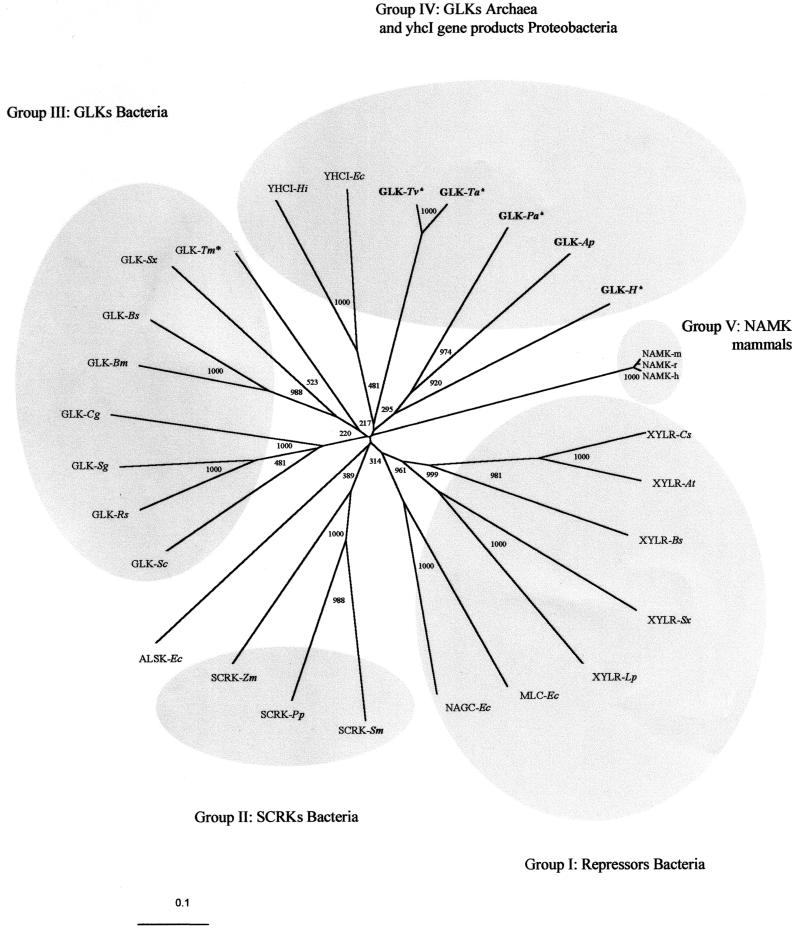
FIG. 5.
Phylogenetic relationships among ROK proteins. The tree was generated by the neighbor-joining method of Clustal X (55). Bootstrap values are based on 1,000 replicates and are given at each node. Archaeal sequences are marked in boldface, and putative sequences are marked with an asterisk. Sequence accession numbers are shown in parentheses. Group I abbreviations: XYLRs, xylose repressors; Cs, Caldicellulosiruptor sp. (P40981); At, Anaerocellum thermophilum (Q44406); Bs, Bacillus subtilis (P16557); Sx, Staphylococcus xylosus (P27159); Lp, Lactobacillus pentosus (P21940); NAGC-Ec, N-acetylglucosamine repressor from E. coli (P15301); and MLC-Ec, product of E. coli mlc (P50456). Group II abbreviations: SCRKs, fructokinases; Sm, Streptococcus mutans (Q07211); Pp, Pediococcus pentosaceus (P43468); Zm; Zymomonas mobilis (Q03417); ALSK-Ec, allokinase from E. coli (P32718). Group III abbreviations: Sc, Streptomyces coelicolor (P40184); Rs, Renibacterium salmoni-narum (Q53165); Sg, Streptomyces griseus (Q9F1W1); Cg, Corynebacterium glutamicum (Q9KKE7); Bm, Bacillus megaterium (O31392); Bs, Bacillus subtilis (P54495); Sx, Staphylococcus xylosus (Q56198); Tm, putative Thermotoga maritima (Q9X1I0). Group IV abbreviations: YHCI, gene product of yhcI; Hi, Haemophilus influenzae (P44541); Ec, E. coli (P45425); Tv, putative Thermoplasma volcanicum (Q97AS0); Ta, putative Thermoplasma acidophilum (Q9HJY6); Pa, putative Pyrobaculum aerophilum (PAE3437); H, GLK-H, putative Halobacterium sp. strain NRC1 (Q9HMA7). Group V abbreviations: NAMK-h, N-acetylmannosamine kinase domain of the bifunctional enzyme UDP-N-acetylglucosamine 2-epimerase/N-acetylmannosamine kinase (residues 413 to 722); h, human (Q9Y223); r, rat (O35826); m, mouse (Q9Z0P6).