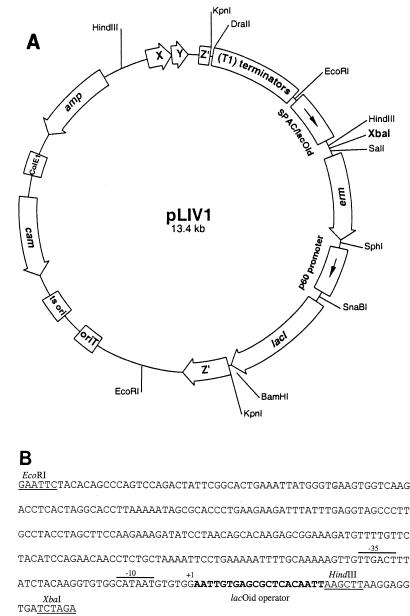
FIG. 1.
Inducible-expression vector for L. monocytogenes. (A) The pLIV1 vector contains the following sequences: a temperature-sensitive origin of replication (ts ori) and a chloramphenicol resistance gene (cam) for plasmid selection in L. monocytogenes, the ColE1 origin of replication and an ampicillin resistance gene (amp) for cloning and selection in E. coli, an origin of transfer (oriT) to allow conjugal mating of plasmid derivatives from E. coli to L. monocytogenes, a unique XbaI restriction site (shown in bold type) for cloning of genes under the transcriptional control of the SPAC/lacOid IPTG-inducible promoter, tandem copies of the rrnB T1 transcription terminator (T1 terminators) upstream of the SPAC/lacOid region to ensure that transcription of cloned genes initiates only by the SPAC promoter, the L. monocytogenes p60 gene promoter to allow constitutive expression of the lac repressor gene (lacI), and an erythromycin resistance determinant within the expression cassette (erm) for selection of inducible constructs on the chromosome. The inducible gene expression cassette is placed within the L. monocytogenes orfZ gene (Z′), which is immediately followed by a putative transcription terminator and flanked by sufficient DNA to allow homologous recombination. Positions of restriction sites utilized for the construction of pLIV1 are indicated (see Materials and Methods). (B) Nucleotide sequence of the SPAC/lacOid promoter/operator region within pLIV1. The −35 and −10 regions of the SPAC promoter are overlined. The transcription initiation site is indicated as +1. The lacOid operator sequence is shown in bold. Restriction sites are noted and underlined.