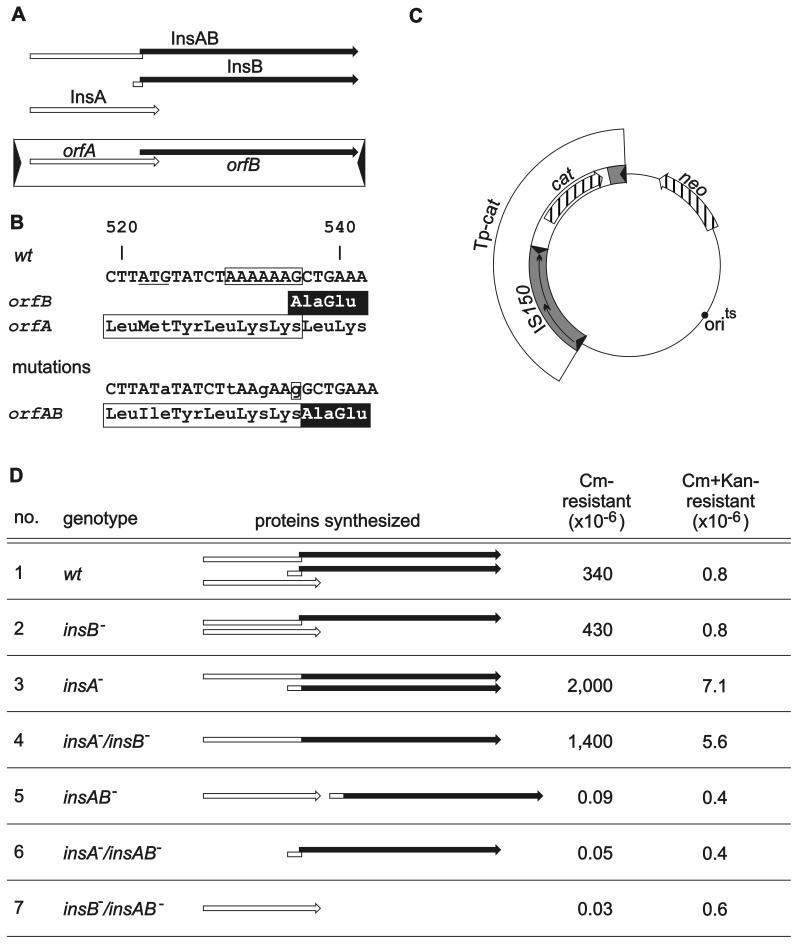
FIG. 1.
Genetic organization of IS150 (A), the mutations (B) introduced into an IS150 driven transposon (C), and the resulting transposition activities (D). (A) The element contains two overlapping open reading frames. The inverted repeats are represented by arrowheads. The three proteins synthesized are represented by the arrows above the element (open arrows, proteins encoded by orfA; solid arrows, proteins encoded by orfB), and the site of programmed translational frameshifting is represented by the offset. (B) At the top the DNA sequence of the region of frameshifting together with the amino acid sequence encoded by orfA (InsA protein) and the amino acid sequence jointly encoded by orfA and orfB after frameshifting (InsAB as well as InsB protein) is shown. The amino acid sequences of the transframe products are indicated by the box (sequence encoded by orfA) and by highlighting (sequence encoded by orfB). The A6G sequence essential for programmed frameshifting is enclosed in a box. The start codon of insB (ATG), arranged in the orfA phase, is underlined. At the bottom is a compilation of nucleotide exchanges and a 1-bp insertion introduced (i) to deactivate frameshifting, (ii) to fuse orfA and orfB, and (iii) to eliminate the insB start codon, together with the effect on the encoded amino acid sequence. Altered nucleotides are indicated by lowercase letters, and the G residue inserted is enclosed in a box. (C) Relevant structures of the IS150-driven transposon (TP-cat) together with the vector backbone encoding thermosensitive replication machinery and the neo gene as a selection marker. (D) Comparison of the transpositional activity of the TP-cat transposon carrying a wild-type IS150 element (wt) with the transpositional activities of transposons carrying various mutant elements. The IS150 genotypes are indicated on the left and are followed by schematic drawings of the different proteins synthesized by the various elements. The rates are the averages from four to six assays for at least two independent transformants. The deviations were less than 50% from the mean. Cm, chloramphenicol; Kan, kanamycin. The following plasmids were used: transposon 1, pFDX2339; transposon 2, pFDX4107; transposon 3, pFDX3949; transposon 4, pFDX3943; transposon 5, pFDX4104; transposon 6, pFDX4100; and transposon 7, pFDX4106.