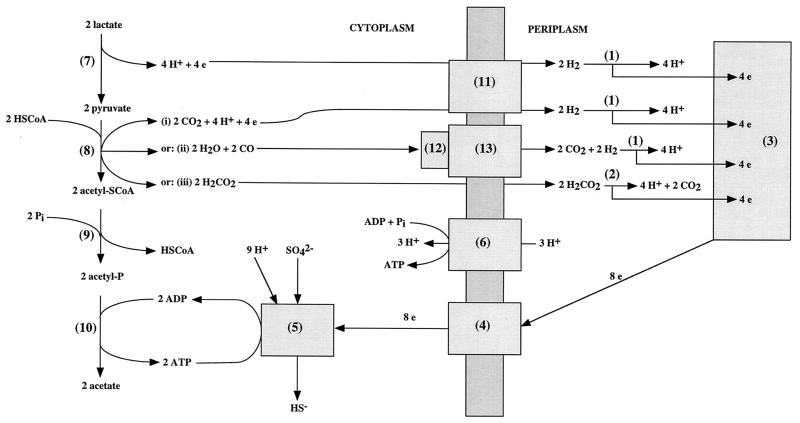
FIG. 1.
Model for ATP synthesis in Desulfovibrio spp. growing on medium containing lactate and sulfate, pyruvate and sulfate, hydrogen and sulfate, or formate and sulfate. The reactions indicated are catalyzed by the following: 1, periplasmic (e.g., Fe-only) hydrogenase; 2, periplasmic formate dehydrogenase; 3, the cytochrome c3 network; 4, transmembrane electron transport (e.g., Hmc) complex; 5, enzymes that reduce sulfate to sulfide (ATP sulfurylase, adenosine phosphosulfate reductase, dissimilatory sulfite reductase, adenylate kinase, and pyrophosphatase); 6, ATP synthase; 7, lactate dehydrogenase; 8-i, pyruvate-ferredoxin oxidoreductase, 8-ii, CO formation from pyruvate (enzyme unknown), 8-iii, pyruvate-formate lyase; 9, phosphotransacetylase; 10, acetate kinase, 11, cytoplasmic, membrane-bound hydrogenase (e.g., Ech [16]); 12, CODH; 13, CO-dependent hydrogenase. CoA, coenzyme A.