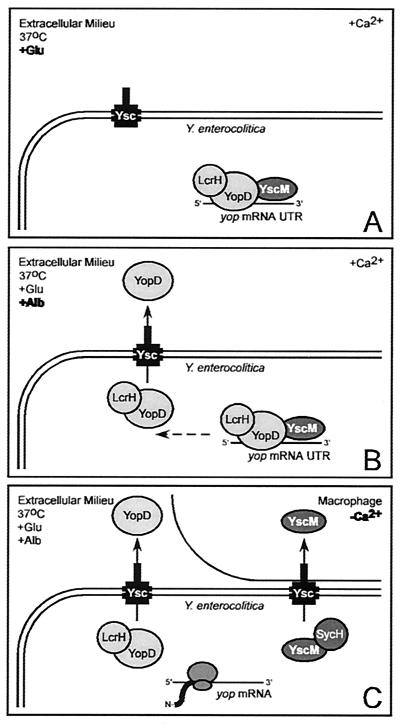
FIG. 11.
Model for the regulation of yop genes by class II gene products. (A) Upon host entry and exposure to 37°C, glutamate (serum amino acid), and 1.2 mM calcium, YopD, LcrH, YscM1, and YscM2 prevent the translation of yop mRNAs by recognizing a feature in the 5′ UTR. (B) Albumin (serum protein) activates the type III secretion of YopD. (C) Insertion of type III needles into the plasma membrane of macrophages triggers a calcium signal that activates the type III targeting of YscM1 and YscM2 via binding to the SycH chaperone. Secretion of YopD and targeting of YscM1 and YscM2 relieve the inhibition of yop mRNA translation and activate Yersinia type III injection of effector Yops.