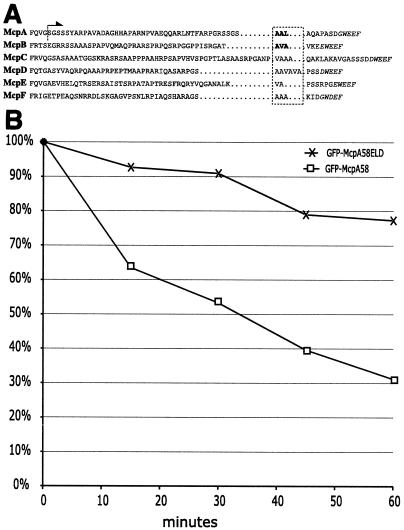
FIG. 6.
Chemoreceptor degradation signal. (A) Amino acid sequences from the exposed C terminus of all C. crescentus MCPs bearing a CheBR binding site were taken from McpA (Q00986), McpB (AAK22415), McpC (AAK22330), McpD (AAK23633), McpE (AAK24252), and McpF (AAK24656). The italicized amino acids indicate the putative pentapeptide CheBR binding site. The boxed hydrophobic amino acids are the putative sequences required for proteolysis. In the McpA and McpB sequences, the bold letters denote hydrophobic residues required for proteolysis as demonstrated by in vitro mutagenesis. The arrow indicates that the amino acid sequence C terminal of the dotted line is present in the GFP-McpA58 fusion. (B) MRKA1280 (GFP-McpA58) and MRKA1281 (GFP-McpA58ELD) cells bearing the xylose inducible GFP fusions were grown in PYE medium to an A660 of 0.4 and then the GFP fusions were induced for 2 h by adding 20 mM xylose. After 2 h the cells were centrifuged for 5 min at 5,000 × g and the cells were then resuspended in PYE medium containing 20 mM glucose. This was repeated three times to ensure removal of xylose. Cells from MRKA1280 (GFP-McpA58) and MRKA1281 (GFP-McpA58ELD) were resuspended to an A660 of 0.3 in PYE medium containing 20 mM glucose and grown for 60 min. Equal volumes of cells were taken every 15 min. The cell extracts were analyzed by immunoblotting with GFP antisera (AbCam) and anti-goat horseradish peroxidase (AbCam). The signal generated by Lumi Light Western blotting substrate (Roche) was captured by XLS film (Kodak), which was scanned and quantified using ImageJ (NIH). Each time point was compared with time zero, which was given a value of 100%.