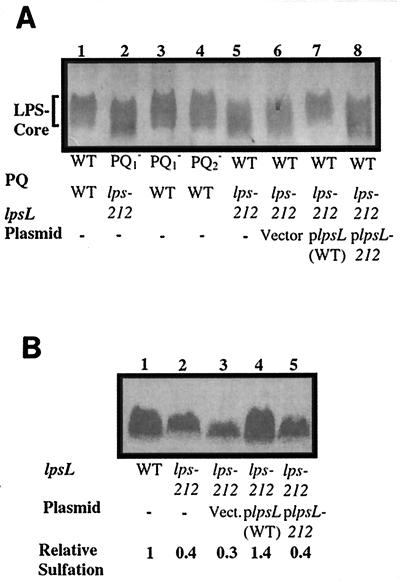
FIG. 1.
Analysis of LPS from wild-type and mutant strains. (A) Silver-stained deoxycholate-PAGE gel of purified LPS core from S. meliloti. Lane 1, strain Rm1021 (wild type [WT]); lane 2, strain JSS12 (nodP1Q1::Tn5-233 lps-212); lane 3, JSS12Tr (nodP1Q1::Tn5-233); lane 4, JSS14 (nodP2Q2::Tn5); lane 5, DKR1 (lps-212); lane 6, DKR58 (lps-212 pVector); lane 7, DKR59 (lps-212 plpsL); lane 8, DKR60 (lps-212 plpsL212). (B) In vivo sulfate labeling of S. meliloti LPS core. Wild-type and lps-212 strains were cultured in the presence of 10 μCi of Na235SO4; the LPS was extracted, fractionated by deoxycholate-PAGE, and analyzed by phosphorimaging as described in Materials and Methods. Lane 1, Rm1021 (wild type [WT]); lane 2, DKR1 (lps-212); lane 3, DKR58 (lps-212 pVector); lane 4, DKR59 (lps-212 plpsL); lane 5, DKR60 (lps-212 plpsL212).