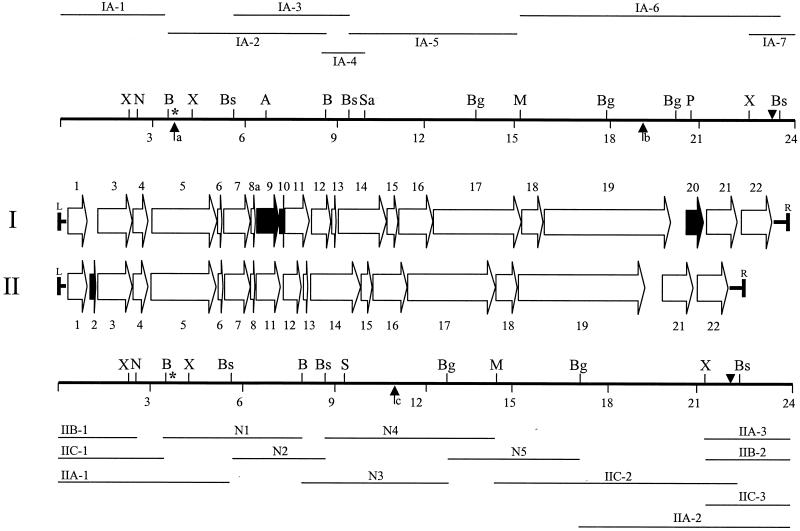
FIG. 2.
Restriction map and ORF complement of the two ICEF configurations in M. fermentans PG18. The locations and directions of ORFs within ICEF units are shown by arrows, and the ORFs are numbered consecutively. Each of the two ICEF configurations (designated I and II) has a slightly different ORF complement; ORFs that are unique to one type of element are shown as black horizontal arrows. The left and right boundaries of the ICEF units are indicated by the letters L and R, respectively. Restriction fragments that have been cloned and sequenced are shown as narrow horizontal lines above (for ICEF-IA) or below (for ICEF-IIA, -IIB, and -IIC) the ORFs. Each fragment is assigned an identifier with a prefix (IA-, IIA-, IIB-, or IIC-) to indicate the ICEF copy from which it was derived or given an N designation if it is an internal fragment that has not been assigned to a specific copy of the type II configuration. Restriction fragments IA-1, IIA-1, IIB-1, IIC-1, IA-7, IIA-2, IIA-3, IIB-2, and IIC-3 contain genomic regions flanking ICE units in addition to the regions of ICE shown. Restriction maps (thick horizontal lines) are shown representing the single type I configuration and the three variants of the type II configuration, with 3-kb size intervals marked below. Abbreviations for restriction sites: A, AflII; B, BamHI; Bg, BglII; Bs, BssHII; M, MluI; N, NheI; P, PstI; S, ScaI; Sa, Sau3AI; X, XbaI. Only the restriction sites used in fragment cloning or hybridization analysis or those that represent characteristic polymorphisms between ICEF configurations I and II are shown. The locations of Southern hybridization probes used in the analyses shown in Fig. 1B (primer 2; asterisks) and C (primer 7; triangles) are shown above the restriction maps. Locations at which comparative sequence analysis revealed the presence of an in-frame stop codon in ORF5 of ICEF-IA (a), a frameshift mutation in ICEF-IA ORF19 (b), and a frameshift mutation in ORF16 (c) within the internal N4 restriction fragment are highlighted by vertical arrows.