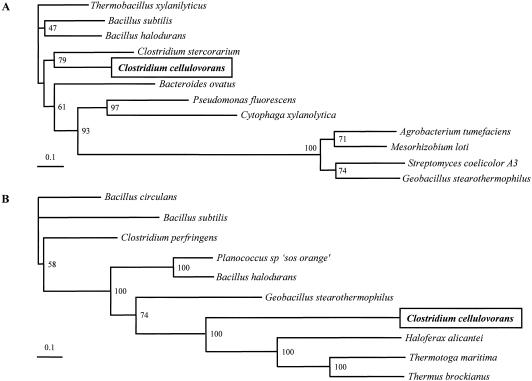
FIG. 2.
Phylogenetic tree of ArfA (A) and BgaA (B) for glycosyl family 51 and family 42, respectively. Phylogenetic trees were constructed using CLUSTAL W with the neighbor-joining method. Results from a bootstrap analysis (n = 100) are shown for the junctions. The following organisms (with GenBank accession numbers) were used as sequence sources for family 51: Thermobacillus xylanilyticus (CAA76421), Bacillus subtilis (P94552), Bacillus halodurans (BAB05593), Clostridium stercorarium (AAC28125), Bacteroides ovatus (Q59219), Pseudomonas fluorescens subsp. (AAK84947), Cytophaga xylanolytica (AAC38456), Agrobacterium tumefaciens (AAL43920), Mesorhizobium loti (BAB50453), Streptomyces coelicolor A3 (CAB86096), and Geobacillus stearothermophilus (AF159625). The following organisms were used as sequence sources for family 42: Bacillus circulans (AAA22260), Bacillus subtilis (CAB15418), Clostridium perfringens (BAA08485), Planococcus sp. ‘SOS Orange’ (AAF75984), Bacillus halodurans (BAB07420), Geobacillus stearothermophilus (P19668), Haloferax alicantei (U70664.2), Thermotoga maritima (NP_229000), and Thermus brockianus (AAD33667).