Figure 1.
Molecular Identification of mudrA and mudrB Homologous Sequences in Various Maize Lines.
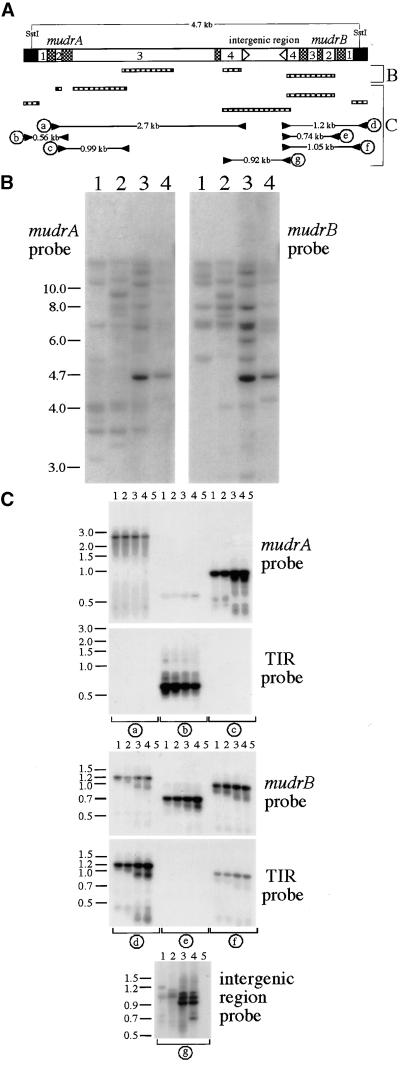
(A) Diagram of the MuDR transposable element. MuDR terminates in nearly identical 215-bp TIRs (black boxes) and contains the convergently transcribed mudrA and mudrB genes, which are annotated with numbers indicating exons, cross-hatched boxes indicating introns, and arrowheads indicating poly(A) addition sites. Bracket B shows MuDR regions recognized by hybridization probes (hatched boxes) used to analyze the diagnostic 4.7-kb SstI fragment (B). Note that the mudrA probe was a mix of two mudrA-specific fragments. The hatched boxes in bracket C are probes (corresponding to components of MuDR) used in hybridization analysis; also shown are the PCR strategy, primer pairs, and expected sizes of successfully amplified products from the mudrA and mudrB genes analyzed in (C). The detailed description of the hybridization probes and PCR analysis can be found in Methods.
(B) DNA samples from mature embryos of two non-Mutator lines, A188/B73 hybrid (lanes 1) and bz2 inbred W23 (lanes 2), and two lines with transcriptionally active MuDR elements, bz2-mu2 (lanes 3) and Robertson's purple Mutator (lanes 4), were digested with SstI and processed by sequential DNA gel blot hybridization as described in (A).
(C) Ten nanograms of genomic DNA from the same maize lines in (B) were analyzed by PCR as described in (A). Lanes 5 are no DNA control samples.