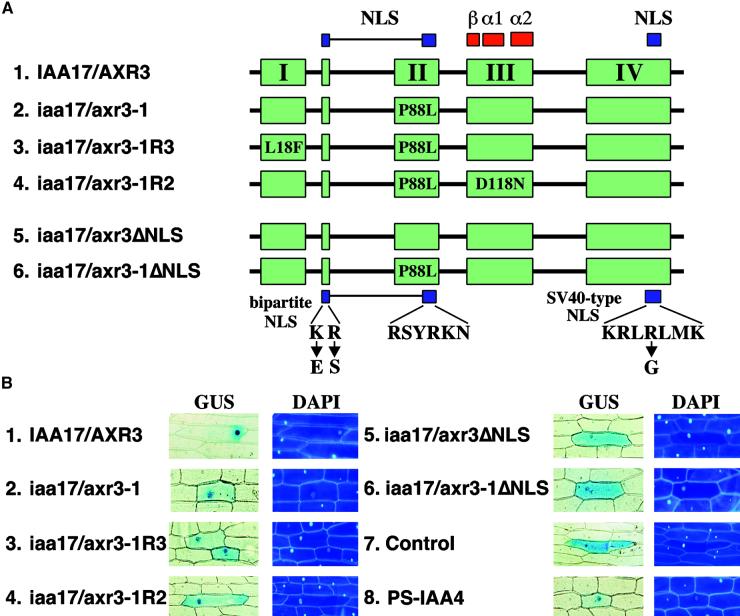
Figure 3.
Nuclear Accumulation of Wild-Type and Mutant Forms of the IAA17/AXR3 Protein.
(A) Scheme of the proteins analyzed. The four conserved domains (I, II, III, and IV) present in the Aux/IAA protein family are shown in green. The two NLS found in these proteins are shown in blue. The location of the prokaryotic βαα protein motif is shown in red. The positions and substitutions of amino acids found in the iaa17/axr3-1 and revertant proteins are shown. The changes corresponding to the mutations were introduced into the IAA17/AXR3 cDNA using the QuikChange method (Stratagene). Shown at the bottom are the substitutions introduced to disrupt the NLS (ΔNLS) of IAA17/AXR3 and iaa17/axr3-1. The different cDNAs were fused in frame with the 3′ end of the GUS cDNA.
(B) Intracellular distribution of GUS fusion proteins. Onion epidermal cells were transformed by microprojectile bombardment using gold particles coated with plasmid DNA. After recovery and staining, cells showing GUS activity were photographed using bright-field optics (GUS); the fluorescence micrographs show the positions of the nuclei in the same cells after staining with 4′-6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI). A plasmid expressing GUS without a functional NLS (Control) was used as a negative control, and a plasmid expressing the nucleus-localized GUS::PS-IAA4 fusion (PS-IAA4) was used as a positive control.