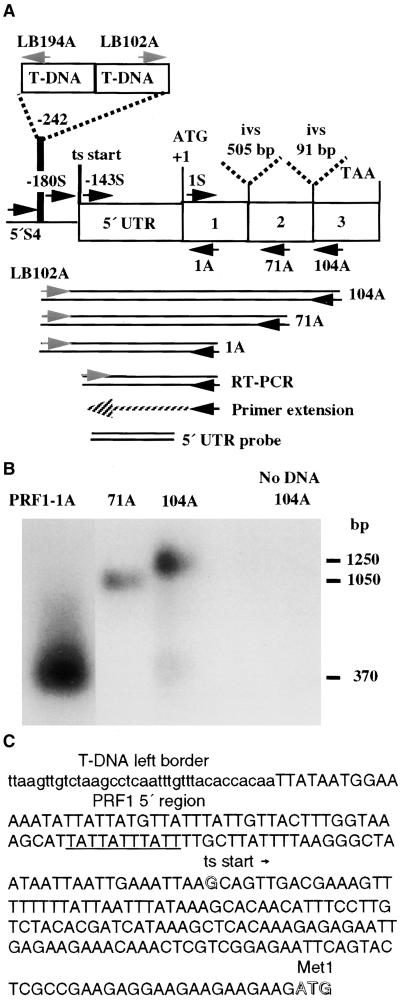
Figure 1.
Characterization of the prf1-1 Mutation and PRF1 Transcripts.
(A) The location of the T-DNA insertion in the prf1-1 mutant is shown on a map of the Arabidopsis profilin gene PRF1. PRF1 encodes a 131–amino acid protein. The locations of primers used in this study are shown, with their 3′ ends indicated by arrows. The PCR products used to map the insertion, the primer extension product and RT-PCR products that were used to map the 5′ end of the PRF1 transcript (ts start), and the 5′ untranslated region (5′ UTR) used as a gene-specific probe are shown below the gene. Two introns (ivs) interrupt the coding region.
(B) prf1-1 mutant plants were identified by a sequence-based screening strategy using a primer (see Table 1) located in the T-DNA left border (LB202) and a degenerate profilin primer, PRF104A, which produced a 1.25-kb product. A ladder of prf1-1/left border junction products is produced by a set of nested antisense profilin primers (PRF104A, 71A, and 1A).
(C) Sequence of the 5′ region of the PRF1 gene (uppercase letters) in the prf1-1 mutant and location of the proximal left border of the T-DNA insertion (lowercase letters). The putative promoter TATA region (underlined), the G residue mapped as the start of transcription (open letter), and the ATG initiation codon (open letters) are indicated.