Figure 7.
The MAPKK-Specific Inhibitor U0126 Compromises Both HarpinPsph-Induced SIPK Activation and PR Gene Expression in Tobacco.
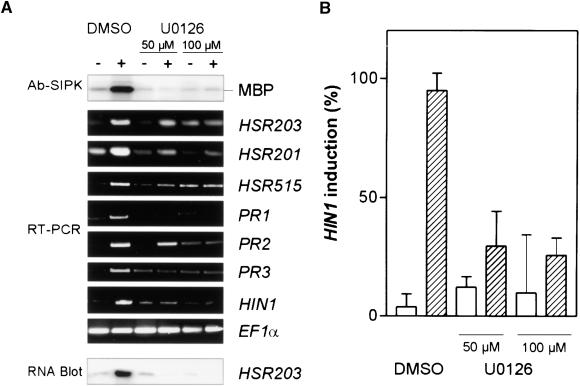
(A) Tobacco cells were treated for 3 hr with buffer (−) or 1 μM harpinPsph (+) in the absence (DMSO) or presence of 50 or 100 μM U0126, a MAPKK-specific inhibitor (Favata et al., 1998). The highest concentration of DMSO used was 0.2%. Protein extracts from elicited tobacco cells were analyzed for SIPK activity as described in the legend to Figure 5C. The expression of PR genes was analyzed by RT-PCR with total RNA and specific DNA primers for the indicated genes or, alternatively, by RNA gel blot analysis using total RNA and α-32P-dATP–labeled HSR203 cDNA.
(B) Quantification of the inhibitory effect of U0126 on harpinPsph-induced HIN1 expression. RT-PCR products obtained from three independent elicitation experiments as described in (A) were separated electrophoretically, blotted onto nylon membranes, and probed with α-32P-dATP–labeled HIN1 cDNA. The signal intensity was quantified by phosphorimaging and normalized to 100% for the maximum induction in each experiment. Buffer treatment (blank bars); harpinPsph treatment (shaded bars). Error bars indicate ±se.