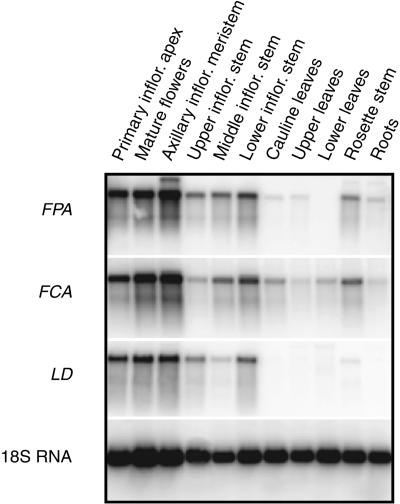
Figure 4.
Reverse Transcription–PCR Analysis of FPA, FCA, and LD Expression Patterns.
FPA, FCA, and LD expression patterns were determined by reverse transcription–PCR. Twenty-five cycles of PCR amplification were used for each sample except the control 18S RNA product, which was detected at 17 cycles. Tissue for these experiments was obtained from the Ws accession at 22 days after germination. The inflorescence height at the time of tissue harvest was between 16 and 19 cm. The primary inflorescence (inflor.) apex consisted of the uppermost 3 mm of the inflorescence and contained immature floral buds. Flowers were taken on the day of anthesis. Axillary inflorescence meristem tissue was isolated with 2 mm of stem on either side of the meristem. Upper, middle, and lower inflorescence stem are defined as internode stem sections of the primary inflorescence. The lower stem refers to the first internode from the rosette followed by middle stem and upper stem, respectively. Stem sections did not contain shoot meristems. Cauline leaves are the oldest two leaves of the inflorescence. Upper leaves are defined as the youngest two leaves of the rosette, whereas the lower leaves are the oldest two rosette leaves. Rosette stem was obtained by removing roots, leaves, and the inflorescence from the rosette. Root tissue was isolated from plants grown on sterile medium (see Methods).