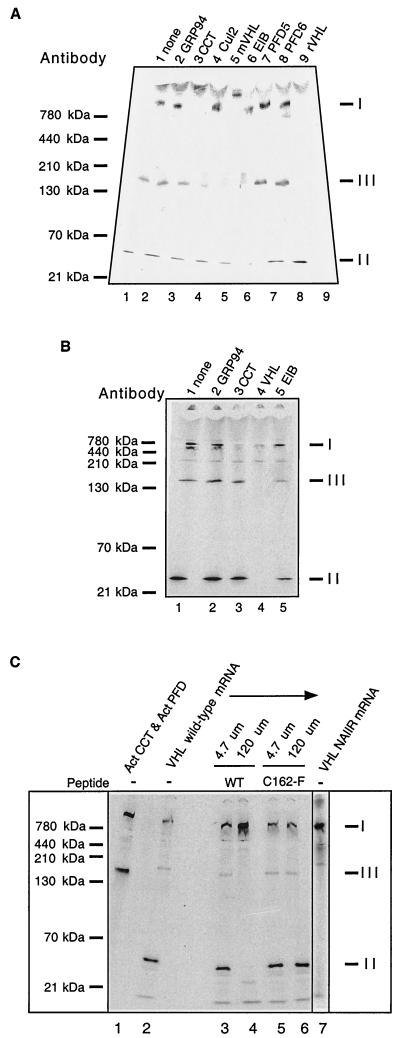
FIG. 2.
Identification of pVHL-containing complexes formed during in vitro translation of VHL mRNA. (A) Antibody-induced gel shifts of pVHL-containing complexes. [35S]methionine-labeled pVHL-containing complexes were generated by in vitro translation of VHL mRNA in the RRL. Cycloheximide then was added to a final concentration of 0.5 mM, and equal aliquots of the reaction products were incubated at 4°C for 30 min with the following antibodies: lane 1, noantibody; lane 2, rat monoclonal anti-GRP94 (negative control); lane 3, rat monoclonal anti-CCT-1α; lane 4, rabbit polyclonal anti-Cul2; lane 5, mouse monoclonal anti-pVHL; lane 6, mouse monoclonal and goat anti-elongin B; lane 7, rabbit anti-prefoldin subunit 5; lane 8, rabbit anti-prefoldin subunit 6; and lane 9, rabbit anti-pVHL. The reaction products were then analyzed by native-PAGE. A fluorogram of the gel is shown. The migration positions of the pVHL complexes are indicated at the right (indicated by I, II, and III), and those of native molecular mass standards are shown on the left. (B) Binding of pVHL-containing complexes to immobilized antibodies. pVHL-containing complexes similar to those in panel A were generated by in vitro translation of VHL mRNA in the RRL. Equal aliquots of the reaction products were incubated at 4°C for 30 min with the following antibodies immobilized on a mixture of protein A- and protein G-Sepharose: lane 1, no antibody; lane 2, rat monoclonal anti-GRP94 (negative control); lane 3, rat monoclonal anti-CCT-1α; lane 4, mouse monoclonal anti-VHL and rabbit VHL antibodies; and lane 5, mouse monoclonal and goat anti-elongin B. Proteins remaining in the unbound fraction were then analyzed by native-PAGE. A fluorogram of the gel is shown. The migration positions of the pVHL complexes are indicated on the right (by I, II, and III), and those of the native molecular mass standards are shown on the left. (C) A peptide derived from pVHL, known to interact with elongin C, blocks the formation of complex II and III and results in the accumulation of VHL with CCT (complex I). VHL mRNA was translated in the presence of [35S]methionine in the RRL for 60 min in the absence or presence of two different synthetic pVHL peptides (at the concentrations indicated at the top). The first peptide was derived from wild-type pVHL (amino acids 157 to 172) and is known to bind to elongin C (WT), and the second was derived from a mutant form of pVHL that fails to interact with elongin C (C162F). The lane on the far right contains the products of a translation reaction programmed with VHL mRNA encoding a mutant that contains an insertion of the sequence NAIIRS in the elongin C binding region of pVHL. A fluorogram of the native gel is shown. The migration positions of native molecular mass standards are indicated at the far left. For reference purposes, a reaction wherein newly synthesized actin bound to both CCT and prefoldin is included in the first lane. The position of migration of the pVHL complexes is indicated on the right (I, II, and III).