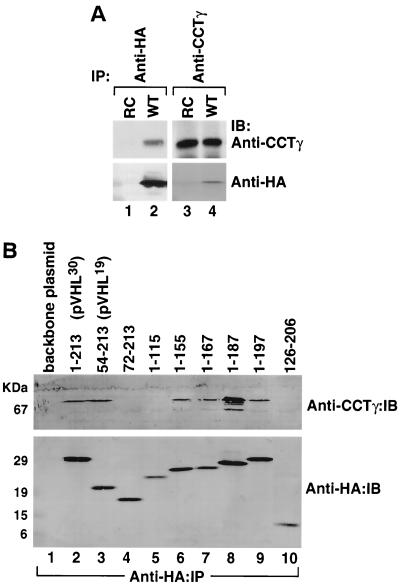
FIG. 4.
(A) Interactions of wild-type and mutant pVHL with the cytosolic chaperonin in vivo. RCC 786-O cells (lacking endogenous pVHL) transfected with and stably expressing HA-tagged wild-type pVHL (WT) or cells transfected with empty plasmid (RC) were lysed and used for immunoprecipitation reactions (IP) employing an anti-HA antibody (lanes 1 and 2) or an anti-CCTγ antibody (lanes 3 and 4). The resultant pVHL immunoprecipitates were resolved by SDS-PAGE, transferred onto a polyvinylidene difluoride membrane, and then immunoblotted (IB) with anti-CCTγ (top panels) or anti-HA (bottom panels) antibodies. (B) The region encompassing amino acids 54 to 155 of pVHL contributes to the binding of CCT. RCC 786-O cells expressing HA-tagged versions of either wild-type pVHL or a series of pVHL deletion mutants were lysed and used for immunoprecipitation reactions with the anti-HA antibody. The resultant pVHL immunoprecipitates were resolved by SDS-PAGE, transferred to a polyvinylidene difluoride membrane, and then analyzed for the presence of both the cytosolic chaperonin (Anti-CCTγ:IB) and HA-pVHL proteins (Anti-HA:IB) via Western blotting. The amino acids included in each pVHL polypeptide are listed at the top. Lane 1 represents cells transfected with empty plasmid. p30 represents the full-length pVHL that was initiated at the first methionine codon, while p19 represents a naturally occurring pVHL that was initiated at the second methionine codon.