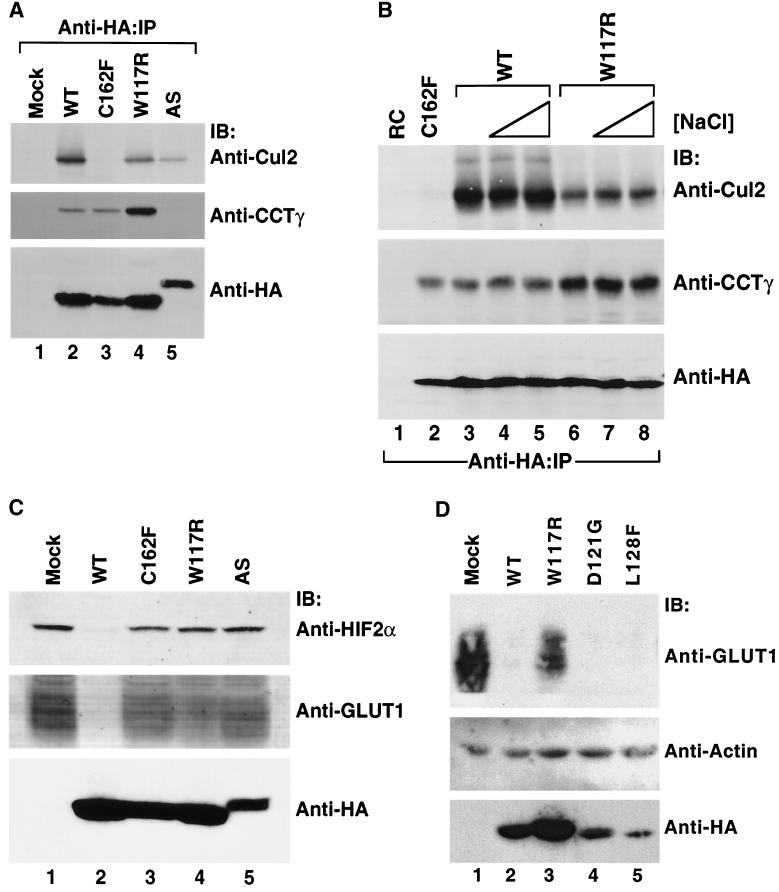
FIG. 7.
Stability and function of wild-type and representative exon II mutant pVHL polypeptide complexes with CCT and elongin B/C-Cul2 formed in vivo. (A) Effects of mutations in VHL exon II upon pVHL-CCT and VCB assembly. RCC 786-O cells expressing empty plasmid (Mock) or HA-tagged versions of wild-type or mutant pVHL were lysed and then immunoprecipitated with the anti-HA antibody (Anti-HA-IP). Resultant immunoprecipitates were resolved by SDS-PAGE and then Western blotted with anti-Cul2 (top panel), anti-CCTγ (middle panel), and anti-HA (bottom panel) antibodies. The particular pVHL polypeptide synthesized is indicated at the top of the panel. (B) Effects on stability of pVHL-CCT and VCB-Cul2 complexes. RCC 786-O cells expressing HA-tagged wild-type pVHL (WT) (lanes 3 to 5) or an exon II pVHL point mutant (W117R) (lanes 6 to 8) were lysed and immunoprecipitated with the anti-HA antibody under increasing NaCl concentrations (125 mM [lanes 1, 2, 3, and 6], 500 mM [lanes 4 and 7], and 900 mM [lanes 5 and 8]). Lysates from cells transfected with plasmid alone (RC) (lane 1) and the HA-tagged exon III mutant (C162F) (lane 2) were immunoprecipitated with the anti-HA antibody under the lowest NaCl stringency condition. Proteins present within the immunoprecipitates were resolved by SDS-PAGE, transferred to nitrocellulose, and analyzed via Western blotting (IB) with the anti-Cul2 (top panel), anti-CCTγ (middle panel), and anti-HA (bottom panel) antibodies. (C) Exon II mutants that do not bind to HIF in the in vitro assays are unable to suppress expression of a HIF 2α regulated gene product, GLUT1. In parallel, the same cell lysates analyzed in B were examined for their expression of HIF-2α and GLUT1, a gene product whose expression is regulated by the HIF-2α transcription factor. Whole-cellextracts were prepared from the cells described above, and the proteins (200 μg) were resolved by SDS-PAGE and then Western blotted (IB) with anti-HIF-2α (top panel), anti-GLUT1 (middle panel), or anti-HA (bottom panel) antibodies. The GLUT1 protein likely appears as a rather diffuse band due to heterogeneity in its glycosylation and because of its many (>10) transmembrane segments (35, 57). (D) Exon II mutants that do bind to HIF in the in vitro assays are able to suppress expression of an HIF-2α-regulated gene product. RCC 786-O cells were infected with retroviral vectors encoding HA-tagged versions of the wild type or the indicated pVHL mutants. Whole-cell extracts were prepared, and proteins (200 μg) were resolved by SDS-PAGE and Western blotted (IB) with anti-GLUT1 (top panel), anti-actin (middle panel), or anti-HA (bottom panels) antibodies.