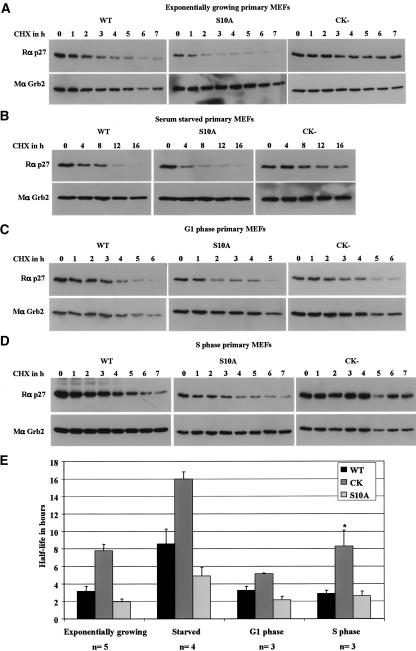
Figure 3.
p27S10A is unstable in quiescent cells, while p27CK– is stabilized in G0 and S phases. p27 half-life determination in exponentially growing (A), serum-starved for 72 h (B), G1-phase (C), and S-phase (D) wild-type (WT), p27S10A (S10A), and p27CK– (CK–) primary MEFs. (A–D) Primary MEFs in the indicated culture conditions were treated with 25 μg/mL cycloheximide (CHX) and collected at the indicated time. A polyclonal p27 antibody (C19), and a monoclonal Grb2 (loading control) were used for immunoblotting. (E) Summary of p27 half-life data from several experiments: exponentially growing (n = 5), serum starved (n = 4), G1 phase (n = 3), and S phase (n = 3). For each experiment, p27 immunoblots were quantified and the amount of p27 expressed as percent of p27 remaining from time zero. Half-lives were determined from the individual graphs by drawing a “best fit” curve for each cell type and condition. (*) Note that the p27CK– half-life in S phase is underestimated in the graph as essentially no turnover occurred during the time frame in one experiment (i.e., T½ ≫ 7 h), and this experiment therefore could not be included in the calculation of half-life.