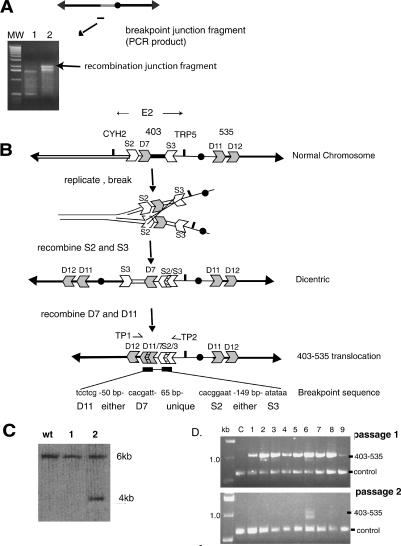
Figure 4.
Isolation and analysis of the DNA sequence of the recombination junction, and a model indicating how the altered chromosome was formed. (A) A PCR technique was used to generate DNA fragments that contain the breakpoint junction (see Materials and Methods). PCR fragments are shown from the original rad9 strain (lane 1) and from one rad9 sectored E2 colony (lane 2; gel images). A ladder of molecular weight standards is shown. The junction fragment is ∼2 kb in size. (B) Interpretation of the structure of the recombination junction. The normal chromosome contains LTR sequence fragments (S2, D7, S3, D11, and D12). The DNA sequence of the breakpoint junction is shown below the 403-535 chromosome. See text for details. (C) Generation of a novel HpaI restriction fragment indicates the presence of the specific 403-535 unstable chromosome. A HpaI digest of DNA from the initial rad9 strain (WT) and from two sectored E2 rad9 colonies (samples 1, 2) was hybridized with a probe to the YGL050 gene (see Fig. 3). Only the preparation in sample 2 has the Hpa1 fragment predicted by the 403-535 chromosome. (D) PCR of translocation junction. Primers (TP1, TP2 in B) were used to amplify a DNA fragment spanning the junction from genomic DNA isolated from a round colony (C) and from nine independent sectored colonies. Passages 1 and 2 are genomic DNA isolated from sectored colonies expanded to ∼109 cells (in 8 mL of minimal media without adenine and tryptophan; passage 1), and then 50 μL of each culture expanded again to ∼109 cells (in 8 mL). Control primers were to YGL044 (see Materials and Methods).