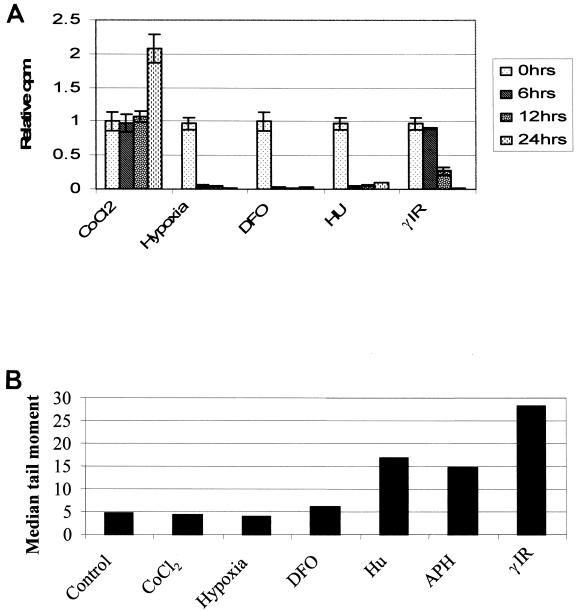
FIG. 7.
Hypoxia induces a rapid intra-S-phase arrest in the absence of any detectable DNA damage. RKO cells were treated with a variety of stresses, and a [3H]thymidine incorporation assay was carried out. The treatments were as follows: hypoxia (0.02% oxygen), 1.5 mM Hu, 8 Gy γIR, 100 μm DFO, and 150 μM CoCl2 for the times indicated. Comet assays were carried out to determine relative amounts of damage caused after each treatment. The median tail moment for each stress is shown. There was no increase in DNA damage over control levels after 24 h of hypoxia or CoCl2 treatment and only a slight increase with DFO. All the other stresses used have DNA damage associated with them to various degrees.