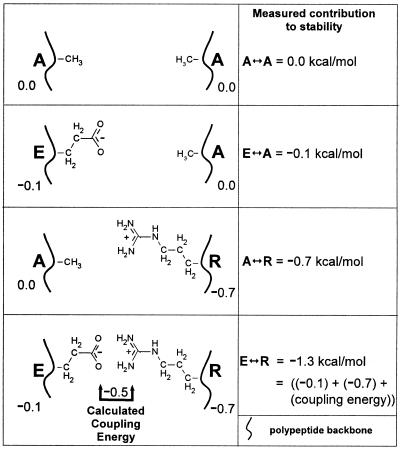
FIG. 5.
Schematic describing the four proteins used for a double-mutant thermodynamic cycle. The top panel depicts two alanines in the g and e′ positions of a g↔e′. The second panel shows that an E↔A pair is 0.1 kcal/mol more stable than an A↔A pair. The third panel shows that a A↔R pair is 0.7 kcal/mol more stable than an A↔A pair. The fourth panel shows a E↔R pair. Instead of being 0.8 kcal/mol more stable than A↔A, as would be expected if the two amino acids did not interact, E↔R is 1.3 kcal/mol more stable. The additional 0.5 kcal/mol is described as the coupling energy indicative of an physical interaction between the E and R side chains.