Figure 1.
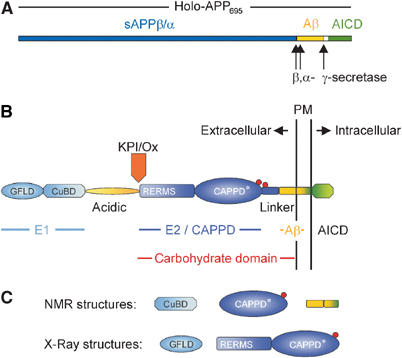
(A) Schematic representation of the holoprotein of human APP695 including the relative position of the α-, β- and γ-secretase cleavage sites. (B) Domain organization of APP: the E1 region consists of the N-terminal growth factor-like domain (GFLD) and the following copper-binding domain (CuBD). The E1 region is linked via the acidic region to the carbohydrate domain, which contains the two N-glycosylation sites of the ectodomain (red spheres). The carbohydrate domain can be subdivided into the E2 domain, also called central APP domain (CAPPD), and a linker or juxtamembrane domain. The carbohydrate domain is followed by the transmembrane and the APP intracellular domain (AICD). Aβ indicates the amyloid β-peptide sequence. The Kunitz-type protease inhibitor domain (KPI), which is present in APP751 and APP770, and the Ox2 sequence, which is present in APP770, are shown above their insertion site. (C) Known stable structures of APP.
