Figure 3.
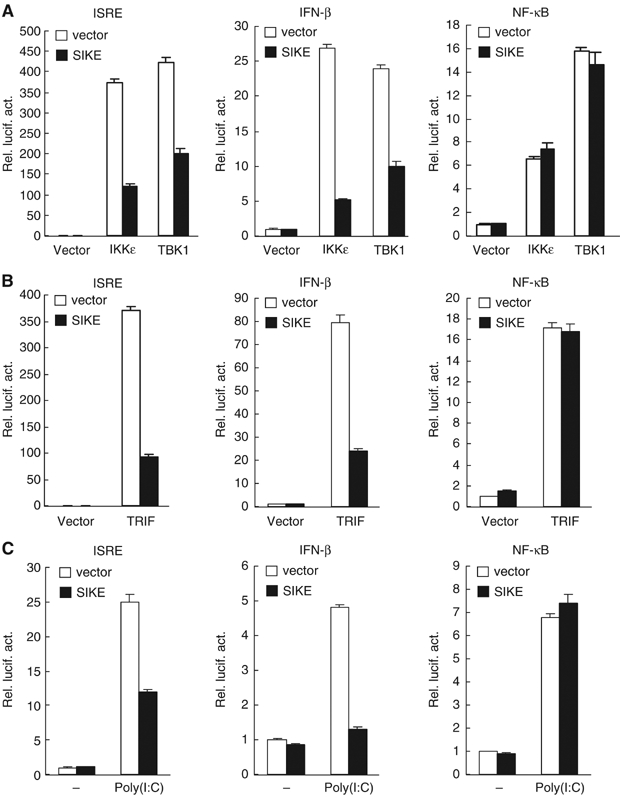
SIKE inhibits IKKɛ-, TBK1-, TRIF- and TLR3-mediated activation of ISRE and the IFN-β promoter but not NF-κB. (A) SIKE inhibits IKKɛ- and TBK1-mediated activation of ISRE and the IFN-β promoter but not NF-κB. The 293 cells (1 × 105) were transfected with the indicated luciferase reporter plasmid (0.1 μg), an expression plasmid for IKKɛ or TBK1 (0.1 μg) and an empty control plasmid (open bars) or an expression plasmid for SIKE (filled bars) (1 μg). Luciferase assays were performed 16 h after transfection. (B) SIKE inhibits TRIF-mediated activation of ISRE and the IFN-β promoter but not NF-κB. The experiments were similarly performed as in (A), except that a TRIF expression plasmid (0.1 μg) was used to replace the IKKɛ or TBK1 plasmid. (C) SIKE inhibits poly(I:C)-induced activation of ISRE and the IFN-β promoter but not NF-κB. The 293-TLR3 cells (1 × 105) were transfected with the indicated luciferase reporter plasmid (0.1 μg) and an empty control vector (empty bars) or a SIKE expression plasmid (filled bars) (1 μg). At 14 h after transfection, cells were treated with poly(I:C) (50 μg/ml) or left untreated for 6 h before luciferase assays were performed.
