Figure 3.
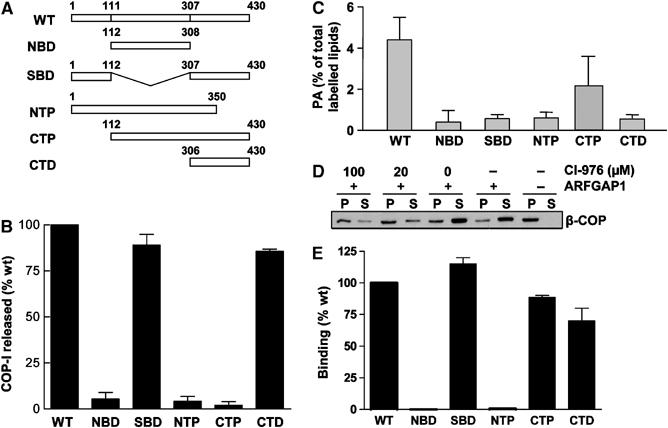
COPI vesicle formation does not require the acyltransferase activity of BARS. (A) Schematic representation of the different domain mutants of BARS. (B) COPI vesicle formation in the presence of different BARS mutants. CHO Golgi membrane washed with 3 M KCl was used for the two-stage incubation system, with the second-stage incubation containing GAP and different forms of BARS as indicated. The level of β-COP released into the supernatant after this stage was quantified, and then normalized to that derived from using the wild-type BARS for incubation. The mean of this normalized value derived from three independent experiments is shown with standard error. (C) Acyltransferase activity of different mutant BARS. The level of phosphatidic acid (PA) generated by the transfer of fatty acyl-CoA onto lysophosphatidic acid, catalyzed by the different forms of BARS, was measured. The mean derived from three independent experiments is shown with standard error. (D) COPI vesicle formation requires an acyltransferase activity. CHO Golgi membrane washed with 0.5 M KCl was used for the two-stage incubation, with the second stage using components as indicated, followed by immunoblotting of pellet (P) and supernatant (S) for β-COP after the second-stage incubation. (E) Binding to GAP by different mutant BARS. GAP fused to GST that had been gathered onto glutathione beads was incubated with different forms of BARS in a pulldown assay. The level of different BARS on beads was quantified, normalized to the level of GAP, and then compared to that of the wild-type BARS. The mean derived from three independent experiments is shown with standard error.
