Figure 4.
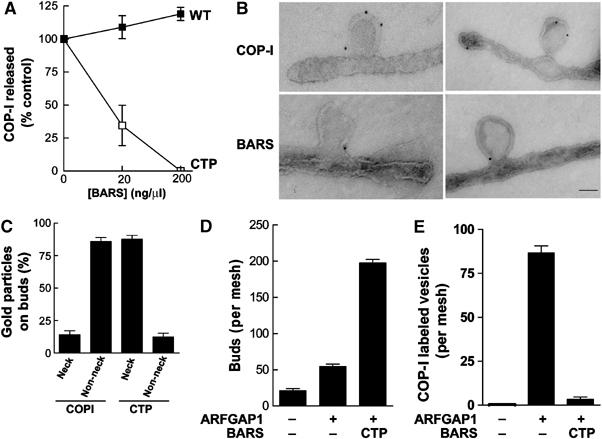
The CTP mutant induces the accumulation of COPI-positive buds on Golgi membrane. (A) The CTP mutant inhibits the reconstitution of COPI vesicles using Golgi membrane washed with 0.5 M KCl. CHO Golgi membrane washed with 0.5 M KCl was used for the two-stage incubation system, with the second-stage incubation containing GAP and varying levels of different BARS as indicated. The level of β-COP released into the supernatant was quantified and then normalized to control, which is derived from the condition that used only GAP in the incubation. The mean of this normalized value derived from three independent experiments is shown with standard error. (B) The CTP mutant induces the accumulation of COPI-positive buds on Golgi membrane. CHO Golgi membrane washed with 0.5 M KCl was used for the two-stage incubation system, with GAP and CTP added at the second stage, followed by EM examination using anti-COPI subunit antibodies (upper panels) and anti-BARS antibody (lower panels); bar, 50 nm. (C) CTP localizes mostly to the neck of buds on Golgi membrane. Ten fields from the EM that resulted (B) were randomly selected for quantitation of the level of gold particles on either the neck region of the bud or the rest of the bud, and then expressed as fractional levels. The mean derived from three independent experiments is shown with standard error. (D) Quantitation of COPI-positive buds on Golgi membrane induced by the CTP mutant. The two-stage incubation system was performed using Golgi membrane washed with 0.5 M KCl, followed by EM examination with labeling using anti-ɛ-COP and anti-ζ-COP antibodies. For each condition, five meshes were randomly selected for counting. The mean derived from three independent experiments is shown with standard error. (E) CTP inhibits COPI vesicle formation. The same quantitation as described above (D) was carried out assessing for vesicles rather than buds.
