Figure 5.
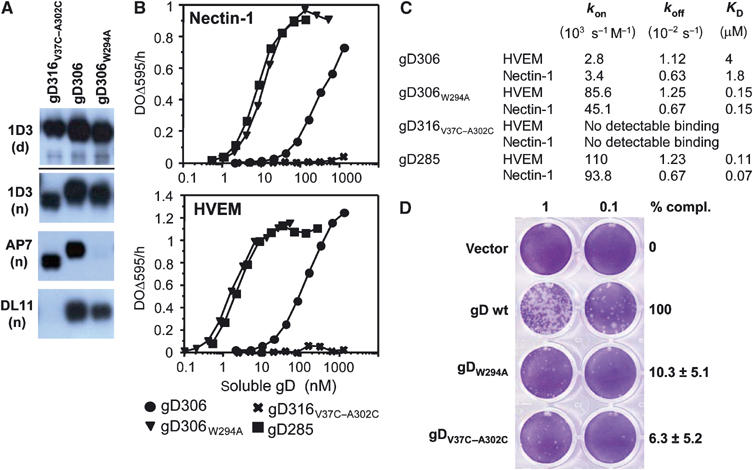
Biochemical and functional characterization of gD mutants. (A) Western blots of purified gD ectodomains were probed by various Mabs. Mab 1D3 detects a linear epitope (aa 11–19) under both denaturing/reducing (d) and native conditions (n) electrophoresis. Mabs AP7 and DL11 detect conformation-dependent epitopes under native conditions of electrophoresis. (B) Receptor binding as detected by ELISA. Various concentrations of the indicated forms of purified gD ectodomains were added to immobilized receptor ectodomains (i.e. nectin or HVEM). The bound gD was detected with anti-gD polyclonal serum R7. (C) Kinetic constants (kon and koff) and affinity constant (KD) for gD–HVEM and gD–nectin-1 complexes were measured by surface plasmon resonance and fitted to a 1:1 Langmuir interaction model (see Materials and methods). (D) Complementation of HSV FgDβ with gD mutants and titration of complemented virus on VD60 cells. VD60 cells were stained with crystal violet to visualize plaques. Complemented virus present in the culture medium of transfected–infected cells was undiluted or diluted 10-fold. Titers of complemented viruses are represented as percentage of wt on the right. These numbers are an average of four experiments, including the one presented on the left. Error bars represent ±1 s.d. Vector indicates the use of pcDNA3.1 for transfection as a negative control.
