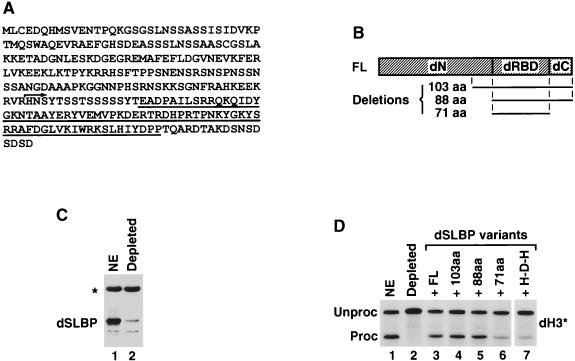
FIG. 6.
Recombinant dSLBP restores processing activity to dSLBP-depleted nuclear extract. (A) Amino acid sequence of dSLBP. The RBD is underlined, and the arrows indicate the starting point of a 103-amino-acid deletion variant. (B) Diagram of the full-length dSLBP (FL) consisting of the N-terminal domain (dN), the Drosophila RBD (dRBD), and the 17-amino-acid end (dC). Regions included in three deletion mutants are shown below. The 103-amino-acid mutant starts 15 amino acids upstream from the Drosophila RBD, as shown in panel A, and contains the remainder of the protein, whereas the 88-amino-acid protein begins with the Drosophila RBD. The 71-amino-acid protein consists only of Drosophila RBD. (C) The S-2 nuclear extract was analyzed by Western blotting before (lane 1) and after depletion with dSLBP antibody (lane 2). The asterisk indicates a cross-reacting protein not removed from the extract during depletion. (D) The dH3∗ histone pre-mRNA was incubated in S-2 nuclear extract (lane 1), in dSLBP-depleted nuclear extract alone (lane 2), or in the presence of the baculovirus-expressed variants, as indicated (lanes 2 to 7). The H-D-H is a hybrid protein consisting of Drosophila RBD and two flanking domains from human SLBP (see Fig. 9A for details).