Figure 7.
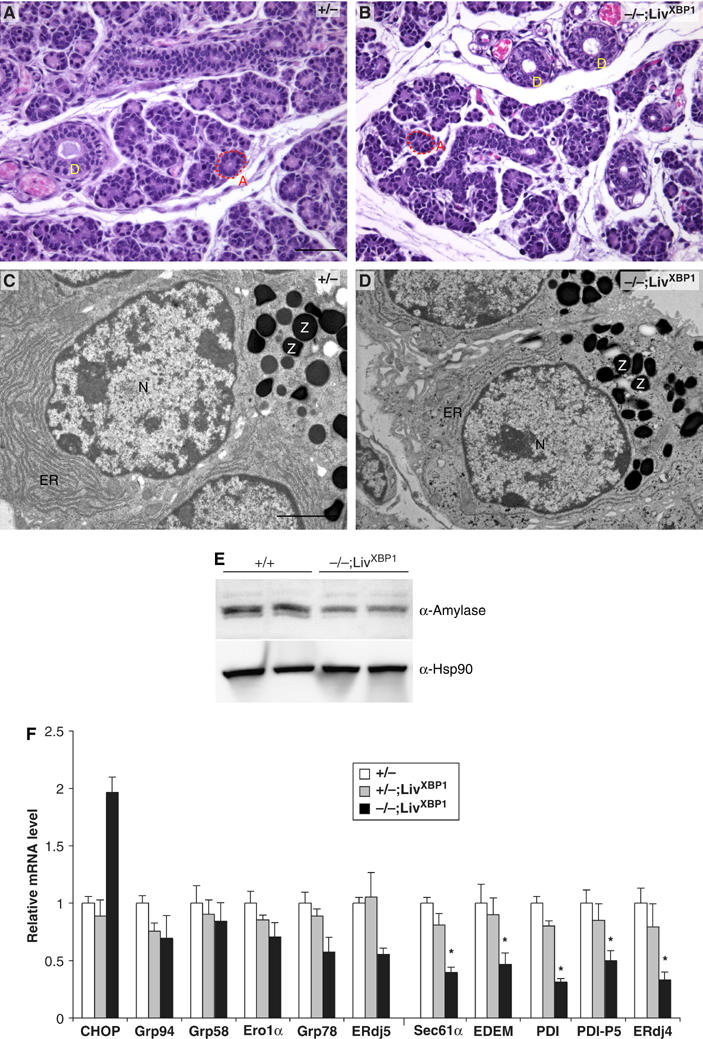
Impaired development of salivary glands in XBP-1−/−;LivXBP1 mice. (A, B) Hematoxylin and eosin staining of the submandibular salivary glands in the control XBP-1+/−;LivXBP1 and mutant XBP-1−/−;LivXBP1 mice. The lobules comprised of secretory acini (A, red dashed lines) appear hypoplastic in the mutant compared to controls. (D) Secretory ducts. (C, D) Electron micrographs of serous salivary glands of control and mutant XBP-1−/−;LivXBP1 mice. Similar to pancreatic acini, these salivary gland acini have well-developed endoplasmic reticulum and apically located zymogen granules (Z). In the mutant, the ER is less well developed but some zymogen granules are produced. (E) Whole-cell lysates of the submandibular salivary glands were subjected to Western blot analysis to measure amylase expression. Scale A and B, 50 μm; C and D, 2 μm. (F) Expression of select XBP-1 target genes and CHOP were measured by real time PCR analysis in WT and XBP-1−/−;LivXBP1 salivary glands. The expression levels of each gene are shown as fold induction over WT. Asterisks indicate genes whose expression was significantly impaired in the absence of XBP-1.
