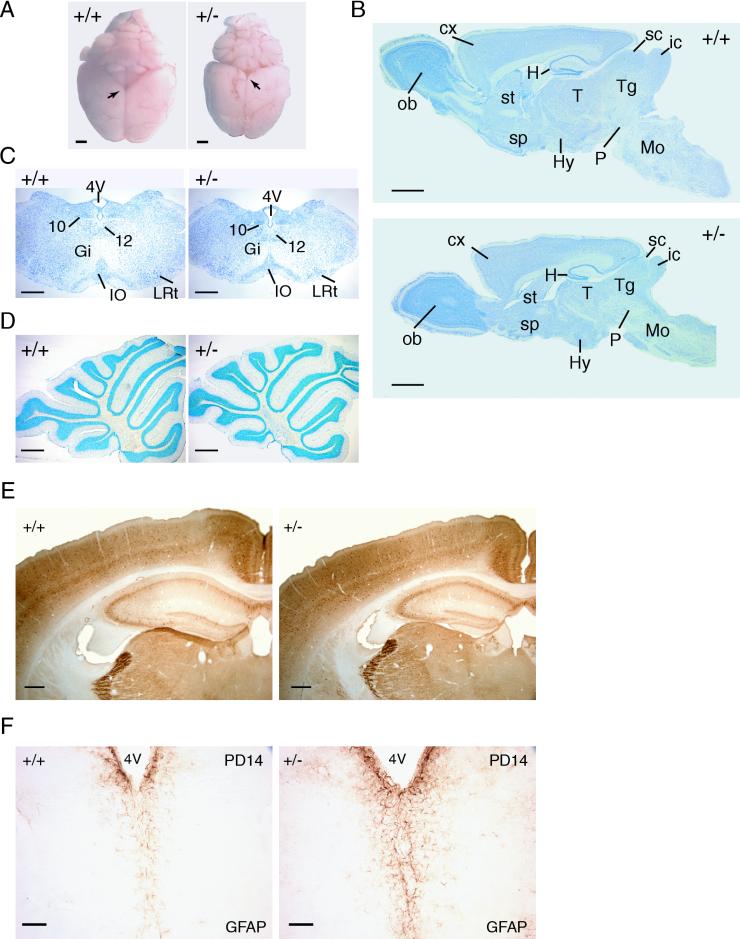
FIG. 4.
Histological characterization of Dyrk1A+/− brains. (A) Dorsal views of brains of wild type (+/+) and Dyrk1A heterozygous (+/−) adult mice. Arrows point to the mesencephalic tectum, which is particularly decreased in +/− brains. Bars, 2 mm. (B) Nissl-stained sagittal sections of +/+ and +/− brains. Abbreviations: cx, cerebral cortex; H, hippocampus; Hy, hypothalamus; ic, inferior colliculus; Mo, medulla oblongata; ob, olfactory bulb; P, pons; sc, superior colliculus; sp, septum; st, striatum; T, thalamus; Tg, tegmentum. Bars, 2 mm. (C) Coronal sections of the medulla oblongata stained with Nissl. A significant decrease is observed in the Dyrk1A+/− section, although all nuclei (10, dorsal motor; 12, hypoglossal; Gi, gigantocellular reticular; IO, inferior olive; LRt, lateral reticular) are present. Bars, 500 μm. (D) Nissl-stained sagittal sections of +/+ and +/− cerebella. The layers and folia of the Dyrk1A+/− cerebellum are found normal. Bars, 500 μm. (E) Coronal sections of parvalbumin-immunostained brains reveal normal lamination of the Dyrk1A+/− cerebral cortex and hippocampus. Bars, 300 μm. (F) GFAP immunostaining in PD14 coronal brain sections shows increased GFAP immunoreactivity in Dyrk1A+/− mice. 4V, 4th ventricle. Bars, 75 μm.