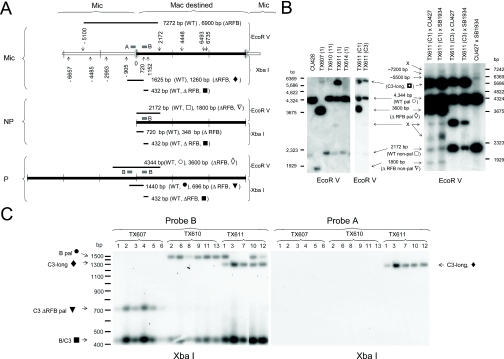
Figure 2.
Heterozygous C3ΔRFB/B strains undergo stochastic excision of the rDNA in the developing macronucleus. (A) Restriction map and fragment sizes for products following digestion with EcoRV (downward arrowheads) or XbaI (upward arrowheads) for micronuclear rDNA locus (Mic), excised non-palindromic macronuclear rDNA (NP) and palindromic (P) rDNA minichromosomes derived from wild-type B rDNA (WT) or C3ΔRFB deletion alleles. Hybridization probes A and B: thick black lines in micronuclear rDNA diagram. (B) Stochastic appearance and structure of macronuclear C3 rDNA in clonal C3ΔRFB transformants. Left panel: Southern blot analysis of EcoRV digested genomic DNA with probe B. Wild-type B rDNA strain; CU428, heterozygous C3ΔRFB/B germline transformant strains; TX607(1), TX610(11) and TX611(1), and wild-type C3 rDNA transformant strain; TX614(1). The position of wild-type B and wild-type C3 rDNA monomers (WT non-pal) and palindromes (WT pal), predicted C3ΔRFB species (ΔRFB pal, ΔRFB non-pal), and unexpected products (C3-long and X) are indicated. The corresponding restriction fragments for expected products are symbol coded (see panel A). TX611(C1) and TX611(C3) are clonal progeny derived from a cross between TX611(1) and amicronucleate strains A* III and A* V, respectively, and have generated a new macronucleus by round II genomic exclusion (see text). Note the presence of the C3ΔRFB rDNA palindrome in TX611(C1) and absence of this species in its parent, TX611(1). Right panel: Southern blot analysis of genomic DNA with probe B from mating progeny harvested 24 h after mixing strains of opposite mating type. Crosses: TX611(C1) or TX611(C3) were mated with tester strains, CU427 (wild B rDNA in micronucleus) or SB1934 (wild-type C3 rDNA in micronucleus). Control mating: CU427 × SB1934. X indicates rDNA species that were not predicted by conventional processing at the Cbs element upstream of the rDNA 5′ NTS. (C) The C3-long rDNA species is fragmented at a novel site upstream of the 5′ Cbs element. Southern blot of XbaI digested genomic DNA hybridized with probe B (left) or probe A (right). Numbers correspond to clonal lines established from each heterozygous C3ΔRFB/B rDNA germline transformant.