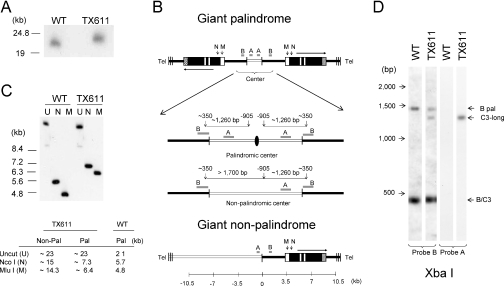
Figure 3.
The macronuclear rDNA species, C3-long, is a giant head-to-head inverted repeat with a palindromic central region. (A) Pulse field gel analysis of undigested total genomic DNA from wild-type (CU428) and ‘C3-long’ ΔRFB [TX611(1)] strains hybridized with probe B. (B) Restriction maps for three possible ‘C3-long’ macronuclear rDNA configurations: giant inverted repeat with a palindromic center (top), giant inverted repeat with a non-palindromic center (middle) and giant monomer (bottom). Black lines: macronuclear-destined 5′ NTS sequences in wild-type minichromosomes; open lines: upstream sequences that are not associated with wild-type macronuclear rDNA. The enlarged central region in the rDNA palindrome maps exhibit the position of XbaI sites (vertical arrows) and predicted restriction fragments that would be detected with probes A or B for molecules with palindromic or non-palindromic central cores. The black oval corresponds to the axis of symmetry for the species with a palindromic center. Note that probe B spans the XbaI site in the normal 5′ NTS. (C) Southern blot hybridization of uncut (U), MluI (M) or NcoI (N) digested DNA with probe B. Note: The apparent slower migration of uncut wild-type control DNA is a gel electrophoresis artifact (‘smiling’). The table shows the expected fragment sizes for monomeric (non-pal) and palindromic C3-long species. (D) Southern blot hybridization of XbaI- digested DNA with probes A and B (see panel B map for predicted product sizes for molecules with palindromic or non-palindromic centers).