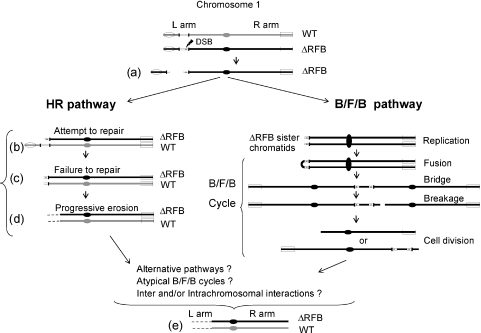
Figure 7.
Models for the loss of the rDNA gene, progressive loss of the 1L chromosome arm and subsequent loss of 1R DNA sequences in heterozygous C3ΔRFB/B rDNA strains. Each micronucleus contains one copy of wild-type (WT) and mutant (C3 ΔRFB) rDNA in the respective chromosome 1 homologs. The jagged arrow in the mutant chromosome indicates a fragile site that induces a DSB (a). In one model (left), the attempted repair the DSB in the mutant chromosome by homologous recombination (HR) involves alignment of both homologs (b). Failure to repair the damaged chromosome induces DSB in the WT chromosome (c). The lack of telomere addition leads to progressive loss of 1L sequences on both homologs (d). The alternative model involves of B/F/B cycles on the fragmented C3ΔRFB chromosome. The DNA complexity generated by B/F/B cycles can be the same as that generated by homologous recombination for the C3ΔRFB allele. Loss of 1R DNA sequences (e) (see text for details).