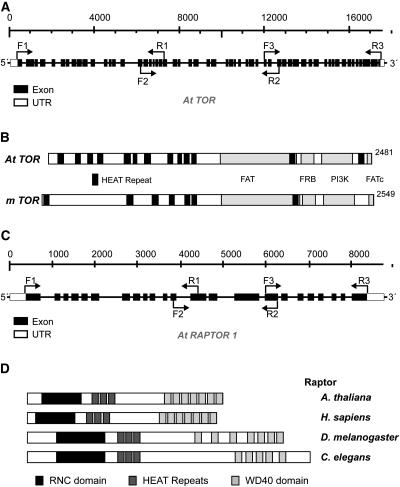
Figure 1.
Cloning of Arabidopsis TOR and RAPTOR1 cDNAs.
(A) Structure of TOR showing exons (black boxes) and intron nucleotide coordinates relative to the start of the gene. Primers used in RT-PCR to clone the TOR cDNA are indicated next to the bent arrows. UTR, untranslated region.
(B) Conserved protein domains found in Arabidopsis TOR, in comparison with mammalian TOR (mTOR). Different domains are indicated with the labeled boxes in black and gray.
(C) Structure of RAPTOR1 showing exons (black boxes) and intron nucleotide coordinates relative to the start of the gene. Primers used in RT-PCR to clone the RAPTOR cDNA are indicated next to the bent arrows.
(D) Conserved protein domains found in different RAPTOR homologs.