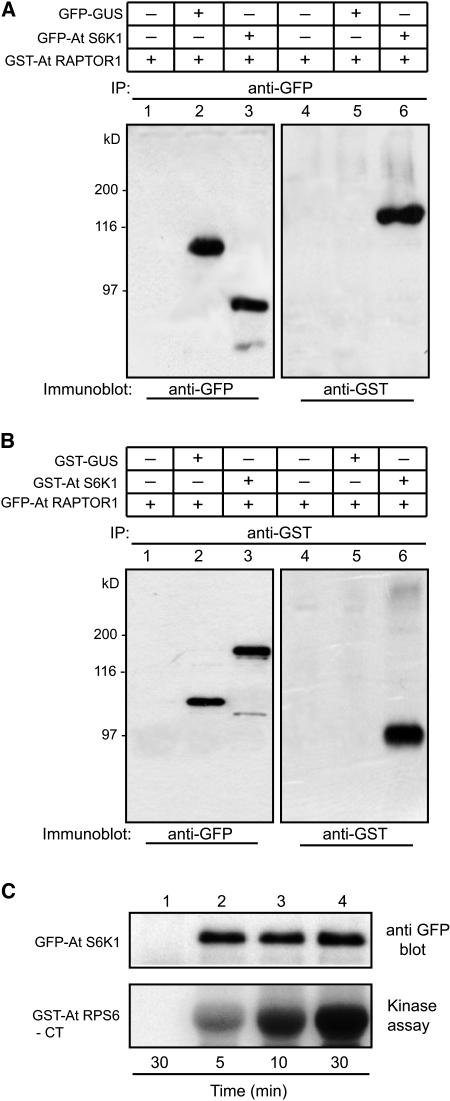
Figure 4.
Ectopically Expressed S6K1 Is Active and Interacts in Vivo with RAPTOR1.
(A) 35S:GFP-S6K1 and 35S:GST-RAPTOR constructs were expressed in tobacco (N. benthamiana) leaves by agroinfiltration. Proteins were immunoprecipitated with GFP antibody, and the same fractions were immunodetected by GFP antibody (lanes 1 to 3) and GST antibody (lanes 4 to 6). Lanes 1 and 3, a negative control for immunoprecipitation with GST-RAPTOR1 expressed alone; lanes 2 and 4, control for interaction specificity with GFP-GUS coexpressed with GST-RAPTOR1; note the presence of RAPTOR1 as a coimmunoprecipitant of S6K1 in lane 6.
(B) The reciprocal of the experiment shown in (A). 35S:GST-S6K1 and 35S:GFP-RAPTOR1 were expressed in tobacco leaves by agroinfiltration. Proteins were immunoprecipitated with GST antibody, and the same fractions were immunodetected by GFP antibody (lanes 1 to 3) and GST antibody (lanes 4 to 6). Lanes 1 and 3, a negative control for immunoprecipitation with GFP-RAPTOR1 expressed alone; lanes 2 and 4, control for interaction specificity with GST-GUS coexpressed with GFP-RAPTOR1; note the presence of RAPTOR1 as a coimmunoprecipitant of S6K1 in lane 6.
(C) 35S:GFP-S6K1 expressed in tobacco leaves by agroinfiltration was immunoprecipitated with GFP antibody and subjected to in vitro kinase assay using GST-RPS6-CT as substrate. As a control, 35S:GFP construct expressed and immunoprecipitated with GFP antibody was included in the kinase assay (lane 1). Time in the figure indicates the kinase reaction time at 25°C.