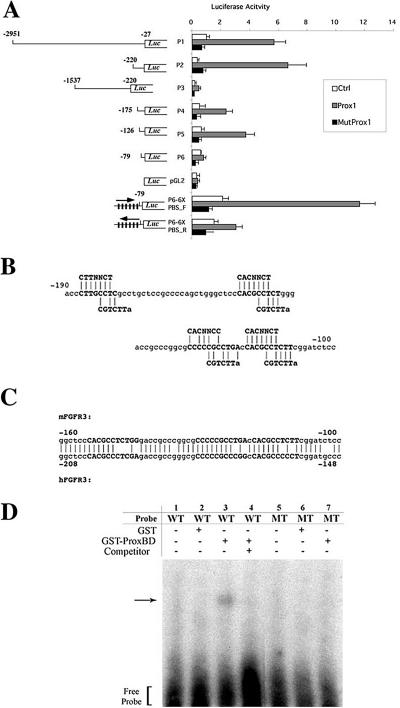
Figure 2.
Prox1 binds to the FGFR-3 promoter to up-regulate its transcription. (A) The FGFR-3 promoter-luciferase (Luc) reporter constructs (P1-P6) and an empty control vector (pGL2) were tested for their luciferase activity in the presence of a vector control (Ctrl), a Prox1-expressing vector (Prox1), or a mutant Prox1-expressing vector (MutProx1). P6-6XPBS contains six-tandem repeats of the Prox1 binding site (PBS, CACGCCTCT) in the P6 construct in the forward- (P6-6XPBS_F) or reverse (P6-6XPBS_R) orientation. Numbers indicate relative locations from the transcriptional initiation site (McEwen and Ornitz, 1998). Data are shown as means ± SD (B) Sequence analysis of the mouse FGFR-3 promoter region revealed four putative Prox1 binding sites. Two previously reported Prospero consensus sequences, C(A/T)(C/T)NNC(T/C) and CGTCTT(A) (Hassan et al., 1997; Cook et al., 2003), are shown above and below the putative Prox1 binding sites (bold), respectively. (C) The proximal three putative Prox1 binding sequences (bold) are conserved between the mouse and human FGFR-3 promoters. (D) Gel electrophoresis mobility shift assays showed that the purified GST-Prox1 fusion protein (GST-ProxBD) but not the GST protein alone binds to the putative Prox1 binding sequences found in the FGFR-3 promoter. The GST or GST-Prox1 proteins were incubated with 32P-labeled a wild-type (WT) or a mutant probe (MT). Arrow indicates a slow migrating complex of GST-Prox1 and the wild-type probe (lane 3). Excessive amount of unlabeled wild-type probe (Competitor) competes for the interaction between GST-Prox1 and the labeled wild-type probe (lane 4).