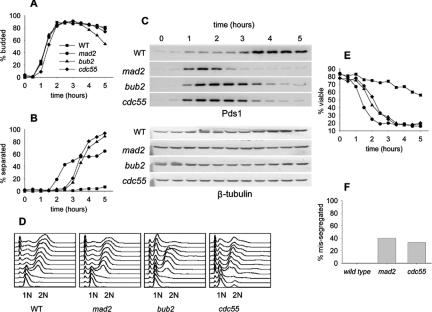
Figure 2.
Response of Cdc55Δ and checkpoint mutants to nocodazole to assay metaphase arrest. Wild-type (8715-10-2), mad2Δ (8715-6-4), bub2Δ (8579-4-4), and cdc55Δ (8778-12-4) cells were synchronized with α-factor, released into YM-1 medium containing 12 μg/ml nocodazole, and sampled at 30-min intervals for a total of 5 h. Cells were limited to a single cell cycle by addition of α-factor at 100 min after release. Symbols for all graphs are as indicated in A. (A) Bud morphology, determined by phase contrast microscopy. (B) Timing of sister chromatid separation at LEU2, determined by GFP fluorescence microscopy. Each time point contains data from 100 cells. (C) Immunoblots of PDS1-13Myc levels to assay the onset of anaphase. (D) Flow cytometry of DNA content to determine the kinetics of replication and cell division. (E) Viability after α-factor block and release into medium containing 15 μg/ml nocodazole at 30°C, as determined by colony-forming ability when returned to YPD agar plates. (F) Segregation fidelity was determined in the same α-factor block and release experiment at 30°C described for Figure 2E. Cells were released into medium containing 15 μg/ml nocodazole, removed at the 2-h point, washed, and returned to liquid medium lacking nocodazole for 1 h. Cells were fixed, and GFP and 4,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) were visualized. Missegregation is the percentage cells that have undergone full nuclear division into mother and daughter cells but have segregated both copies of GFP-labeled chromosome 3 into the same nucleus.