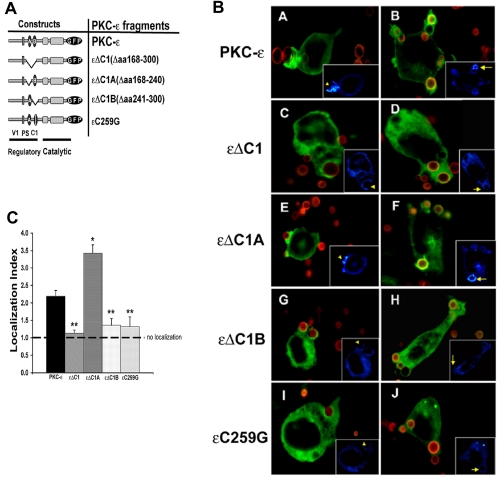
Figure 2.
εC1B is necessary for localization to BIgG targets. (A) Constructs used in these studies: V1, variable region 1; PS, pseudosubstrate; C1, constant region 1 containing the lipid binding regions C1A and C1B. (B) Localization to BIgG. Indicated constructs were expressed in RAW 264.7 cells, and transfectants were incubated with Alexa 568-labeled BIgG. Phagocytosis was terminated at 5–7.5 min, the cells were fixed, and the fluorescence was analyzed with postacquisition deconvolution software. Protein kinase C-ε and εΔC1A concentrated at IgG-opsonized targets, whereas εΔC1, εΔC1B, and εC259G did not. Left, protein kinase C-ε distribution in cells containing forming phagosomes (concentration seen in protein kinase C-ε and εΔC1A expressing cells). Right, distribution of GFP conjugates in cells containing fully internalized particles (protein kinase C-ε and εΔC1A-expressing cells retain membrane localization). Insets, pseudocolor images of GFP pixel intensity (concentration visualized as white; blue represents minimal pixel intensity). (C) Quantitation of phagosomal localization. Localization index = GFP fluorescence of phagosomal membrane/nonphagosomal membrane in transfectants expressing the indicated protein kinase C-ε constructs. Data are presented as mean ± SEM (30–40 phagocytic events from four independent experiments). *p < 0.00003, **p < 0.00002 compared with full length protein kinase C-ε (Videos 1–3).