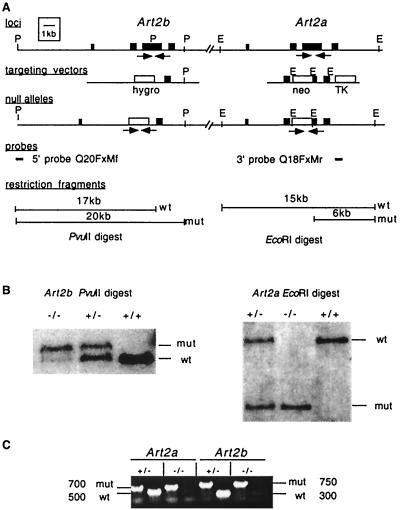
FIG. 2.
Disruption of the Art2a and Art2b genes in ES cells and mice. (A) Schematic representation of the Art2 locus, the Art2a and Art2b targeting vectors, and the targeted Art2 alleles. Filled boxes indicate exons, and labeled boxes indicate the neomycin (neo) resistance, hygromycin (hygro) resistance, and herpesvirus thymidine kinase (TK) cassettes. Homologous recombination of the targeting vectors with the endogenous Art2a and Art2b genes deletes most of the main coding exons. Relevant restriction sites are abbreviated as follows: P, PvuII; E, EcoRI. (B) Detection of targeted and wild-type Art2a and Art2b alleles by Southern blot analyses of genomic DNAs obtained from progeny derived from a heterozygous mating. DNA (5 μg per lane) was digested with PvuII (left panel) or EcoRI (right panel), blotted onto nitrocellulose membranes, and hybridized with the probes indicated by solid lines in panel A. The Art2b 5′ probe detects a 17-kb PvuII fragment from the endogenous Art2b locus and a 20-kb fragment from the targeted locus; the Art2a 3′ probe detects a 15-kb EcoRI fragment from the endogenous Art2a locus and a 6-kb fragment from the targeted locus. (C) Detection of targeted and wild-type Art2a and Art2b alleles by PCR analyses of genomic DNAs obtained from tail biopsies of progeny derived from a heterozygous mating. DNA (50 to 200 ng per lane) was subjected to PCR amplification with pairs of primers as indicated by arrows in panel A. These primers amplify a 500-bp fragment from the endogenous Art2a locus and a 700-bp fragment from the targeted locus, and a 350-bp fragment from the Art2b locus and a 750-bp fragment from the targeted locus.