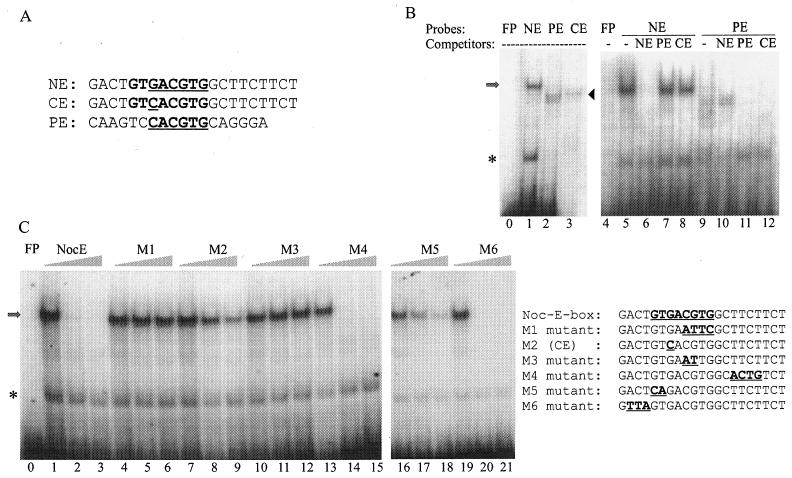
FIG. 2.
NE sequence as defined by EMSAs. (A) Sequence alignment of the NE, CE, and PE. (B) EMSAs were performed with a nuclear extract mixture isolated from Xenopus retina at ZTs 2 and 14. The identities of the radiolabeled probes and 100-fold-molar-excess cold competitors are given at the tops of the lanes. The arrow and arrowhead mark the positions of specific DNA-protein complexes revealed when NE and PE, respectively, were used as probes. The asterisk indicates nonspecific binding activities. (C) The NE was used as the probe in all lanes. Identities of the competitors are given at the tops of the groups of three lanes. Each group contains 0×, 50×, and 200× concentrations of cold competitors along with the radiolabeled NE probe. The sequences of the probe and competitors are shown to the right of the gels. Note that M2 is identical to CE. Lanes 0 and 4 in panel B and lane 0 in panel C show controls of free probes (FP) without retinal nuclear extracts. Each gel is a representative example of gels from three repeated experiments.